Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
Capases
Cysteine-aspartic acid proteases, are a family of cysteine proteases, which play essential roles in apoptosis (programmed cell death).
-

Carpopedal spasm
Spasm of the hand or foot, or of the thumbs and great toes. A spastic condition of the hands and feet. A spasm in the hands and feet caused by lack of calcium. Involuntary muscular contraction of the hands and feet, sometimes seen in hyperventilation syndrome. It is caused by hypocalcemia and commonly encountered during…
-

Carotenodermia
Yellow skin discoloration caused by excess blood carotene.
-

Carotenoids
A class of natural fat-soluble pigments found principally in plants, belonging to a subgroup of terpenoids containing eight isoprene units forming a C40 polyene chain. Carotenoids play an important potential role in human health by acting as biological antioxidants. Highly pigmented fat-soluble compounds naturally present in many foods. A general term for the wide variety…
-
Carotenes
Are a large group of intense red and yellow pigments found in all plants; these are hydrocarbon carotenoids (subclass of tetraterpenes) and the principal carotene is beta-carotene which is a precursor of vitamin A. The red and orange pigments of plants; all are antioxidant nutrients. Three are important as precursors of vitamin A: α-, β-…
-
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (CPT1)
Also known as carnitine acyltransferase I or CAT1 is a mitochondrial enzyme, involved in converting long chain fatty acid into energy. An essential enzyme crucial for the utilization of specific fats as an energy source is known as carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT). Inherited deficiency of this enzyme can result in exercise intolerance-induced rhabdomyolysis, a condition characterized…
-
Carminative
Substance that stops the formation of intestinal gas and helps expel gas that has already formed, relieving flatulence: relieving flatulence or colic by expelling gas. Relieves digestive gas, bloating, and indigestion. An agent that aids the elimination of gas. An agent that relieves and removes gas from the digestive system. An antispasmodic agent used against…
-
Cariogenic
Leading to the production of caries. Causing tooth decay (caries) by stimulating the growth of acid-forming bacteria on the teeth; sucrose and other fermentable carbohydrates. A biological agent that produces tooth decay, caries. Referring to a substance which causes caries.
-
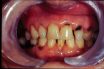
Caries
Tooth decay, commonly called cavities. Dental decay caused by attack on the tooth enamel by acids produced by bacteria that are normally present in the mouth. In dentistry, dental caries or cavities. The medical term for tooth decay, commonly called cavities. Breakdown and death of tooth tissue, resulting in soft, discolored areas. Studies suggest that…
-
Cardiovascular
Pertaining to the heart and blood vessels. Having to do with the heart and blood vessels. Pertaining to the heart and the blood vessels. Involving the heart (cardio) and blood vessels (vascular). Pertaining to the heart and circulatory system. Referring to the heart and the blood circulation system. The term that signifies “related to the…
Got any book recommendations?