Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
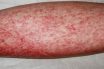
Eosinophilia
The state of having a high concentration of eosinophils (eosinophil granulocytes) in the blood. (Or, less commonly, acidophils), are white blood cells that are one of the immune system components. Granular leukocytes with a nucleus that usually has two lobes connected by a slender thread of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing coarse, round granules that are…
-
Envenomation
Is the entry of venom into a person’s body, and it may cause localised or systemic poisoning. The act of depositing toxins. The use of snake venom as part of a therapeutic treatment. The introduction of venoms into the body by means of a bite or sting. The encounter with venom resulting from insect bites…
-

Enophthalmos
A condition in which the eye falls back into the socket and inhibits proper eyelid function. A condition in which the eyes are very deep in their sockets. Recession of the eyeball into the orbit. Condition in which the eyeball is displaced back in the eye socket, because of injury or developmental defect. A condition…
-
Enuresis
Bed-wetting, a disorder of elimination that involves the voluntary or involuntary release of urine into bedding, clothing, or other inappropriate places. The repeated voiding of urine into bed or clothes in children at least 5 years old, not due to any general medical condition. May be associated with various psychosocial factors, such as early childhood…
-
Entheogen
A substance taken to induce a spiritual experience.
-
Enterotoxigenic
Of or being an organism containing or producing an enterotoxin. Producing enterotoxins, as in some strains of bacteria. The term pertains to a living organism capable of generating toxins within the gastrointestinal system, thereby triggering a range of manifestations including emesis, diarrheal episodes, and various symptoms associated with foodborne illness.
-
Enterotoxin
Is a protein toxin released by a microorganism in the intestine. Substances toxic to the cells of the intestinal mucosa, normally produced by bacteria. A toxin specific for cells of the intestine. Gives rise to symptoms of food poisoning. Toxins excreted by the cells into the gastrointestinal tract of animals. A bacterial exotoxin which particularly…
-
Enteropooling
Increased fluids and electrolytes within the lumen of the intestines due to increased levels of prostaglandins.
-
Enterohemorrhagic
Causing bloody diarrhea and colitis, said of pathogenic microorganisms.
-
Enterocytes
Tall columnar cells in the small intestinal mucosa that are responsible for the final digestion and absorption of nutrients. Terminally differentiated cells comprising the majority of the external surface of the intestinal epithelium. Unlike goblet cells, they do not produce or secrete mucins, nor do they secrete cryptdins as do the paneth cells. The layer…
Got any book recommendations?