Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
Exocytosis
The cellular process by which cells excrete waste products or chemical transmitters. The releasing of an entity that was bound inside an “endosome” (e.g., inside a cell). Process by which cells release compounds such as hormones. The discharge of particles from a cell. They are too large to pass through the cell membrane by diffusion.…
-
Excipient
A pharmacologically inert substance used as a diluent or vehicle for the active ingredients of a medication. Inert vehicle substance in drugs. A substance added to a drug so that it can be made into a pill. A substance that is combined with a drug in order to render it suitable for administration; for example…
-
Excitotoxicity
Is the pathological process by which neurons are damaged and killed by glutamate and similar substances. A condition where neurons are damaged and killed by overactive excitatory neurotransmitter activity. A cascade of neuronal injury that leads to neurodegeneration and dementia. Abnormal stimulation of the central nervous system (CNS) following a traumatic stimulus, such as a…
-
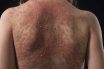
Exanthematous
Characterized by or of the nature of an eruption or rash. Referring to an exanthem or like an exanthem.
-
Euglycaemia
Normal blood glucose concentration.
-
Estrus
Sexual excitement or heat of female; or period of this characterized by changes in the sex organs. A recurrent period of sexual receptivity in female animals marked by an intense sexual urge. Slang: in heat. The portion or phase of the sexual cycle of female animals characterized by a willingness to accept the male. Periodic…
-
Estrogenic
Relating to estrogen or producing estrus. Has estrogen-type hormonal activity within the body. With a similar action to estrogen in the body, supporting and maintaining the female reproductive organs. A substance that induces female hormonal activity and that binds to and activates cells sensitive to the human hormone estrogen, which is found in the breasts…
-
Estrogen receptor negative (ER-)
Tumour is not driven by estrogen and need another test to determine the most effective treatment.
-
Estrogen receptor positive (ER+)
Means that estrogen is causing the tumour to grow, and that the breast cancer should respond well to hormone suppression treatments.
-
Estrogen receptor (ER)
Is a protein found in high concentrations in the cytoplasm of breast, uterus, hypothalamus, and anterior hypophysis cells; ER levels are measured to determine a breast CA’s potential for response to hormonal manipulation. A cellular protein that binds female sex steroid hormones. When estrogens attach to it, they stimulate cells to transcribe DNA and manufacture…
Got any book recommendations?