Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-

Favus
A chronic skin infection, usually of the scalp, caused by the fungus, Trichophyton schoenleinii and characterized by the development of thick, yellow crusts over the hair follicles. Also termed tinea favosa. A disease caused by infection of hair follicles with Trichophyton schoenleini. A highly contagious type of ringworm caused by a fungus which attacks the…
-
Fauces
The passage leading from the back of the mouth into the pharynx. The throat of the corolla or calyx [unusual term, not recommended]. An opening between the tonsils at the back of the throat, leading to the pharynx. Opening at the back of the mouth into the pharynx. The opening leading from the mouth into…
-
FasL or CD95L
Fas ligand is a type-II transmembrane protein that belongs to the tumour necrosis factor (TNF) family.
-
Familial dysautonomia
A genetic disorder that affects the development and survival of autonomic and sensory nerve cells. Familial dysautonomia (FD), sometimes called Riley-Day syndrome, is a hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy (HSAN). It stems from incomplete development of sensory and autonomic neurons and manifests in widespread sensory and variable autonomic dysfunction (New York University School of Medicine…
-
Familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP)
Also called Corino de Andrade’s disease, a neurodegenerative autosomal dominant genetically transmitted, fatal, incurable disease.
-
Extravasation
Discharge or escape, as of blood from the vein into the surrounding tissues. The act of escaping from a vessel into the tissues as associated with blood, lymph, or serum. Seepage of fluid. A situation where a bodily fluid, such as blood or secretions, escapes into tissue. Leakage of fluid (e.g., blood) to the tissues…
-
Extrapyramidal side effects
Are a group of symptoms (tremour, slurred speech, akathisia, dystonia, anxiety, paranoia and bradyphrenia) that can occur in persons taking antipsychotic medications. An untoward effect of neuroleptic medications with distressing symptoms including tremors, bradykinesia, dystonia, and restless movements of the mouth, legs, and hands.
-
Exteroceptive
Responsiveness to stimuli that are external to an organism. Receiving impressions from outside.
-
Expectorant
An agent that increases bronchial mucous secretion by promoting liquefaction of the sticky mucous and expelling it from the body. Stimulates more effective coughing and clearance of phlegm from the throat and chest. Substance that causes mucus in the lungs and bronchial passages to come out more easily, usually through coughing. An agent that promotes…
-
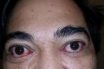
Exophthalmos or exophthalmia or proptosis
Is a bulging of the eye anteriorly out of the orbit. Abnormal protrusion of the eyeball. Prominence of the eyes most commonly found in patients with hyperthyroidism caused by Graves’ disease. Exophthalmos may affect one or both eyes, may be apparent before the overactive thyroid gland develops, and may appear for the first time after…
Got any book recommendations?