Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
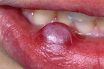
Mucous
Relating to mucus. Having the nature of or resembling mucus. Pertaining to or resembling mucus. A viscous substance generated by the moist membranes that coat numerous body cavities and structures. Characterized by a similarity to mucus.
-
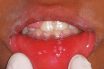
Mucositis
Painful inflammation and ulceration of the mucous membranes lining the digestive tract. A painful inflammatory response of the oral mucous membrane. May be caused by local irritants, including prostheses, or may be systemically induced.
-
MTTP
Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein that is required for the assembly and secretion of triglyceride -rich lipoproteins from both enterocytes and hepatocytes.
-
Morphine
The major alkaloid of opium and a potent narcotic analgesic. A potent opioid analgesic used in medicine to control pain. As with other opiates, morphine’s analgesic effect is exerted directly on the central nervous system (CNS), where the drug interacts with opioid receptors. Tolerance develops with chronic use or abuse, and morphine has a high…
-
Morelloflavone
A biflavonoid extracted from Garcinia dulcis, has shown antioxidative, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Monorrhagia
Is heavy bleeding and that’s usually defined as periods lasting longer than 7 days or excessive bleeding.
-
Monogalactosyl diglyceride
Are the major lipid components of chloroplasts.
-
Monoclonal antibodies
Are produced by fusing single antibody-forming cells to tumour cells grown in culture. Discovered and developed in the 1970s by Cesar Milstein and Georges Kohler, monoclonal antibodies are the name for antibodies derived from a single source or clone of cells that recognize only one kind of antigen. Made by fusing myeloma cancer cells (which…
-
Monoaminergic
Of or pertaining to neurons that secrete monoamine neurotransmitters (e.g., dopamine, serotonin).
-
Monoamine oxidase A (MAOA)
Is an isozyme of monoamine oxidase. It preferentially deaminates norepinephrine (noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline), serotonin, and dopamine. An enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of a large variety of monoamines, including epinephrine, norepinephrine, and serotonm. Monoamine oxidase is found in most tissues, particularly the liver and nervous system. Drugs that act as inhibitors of this enzyme are…
Got any book recommendations?