Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
N-nitrosmorpholine
A human carcinogen.
-
Myotube
A developing skeletal muscle fibre with a tubular appearance. The developing stage of skeletal muscle. The central nucleus occupies most of the cell.
-
Mytonia
A symptom of certain neuromuscular disorders characterized by the slow relaxation of the muscles after voluntary contraction or electrical stimulation.
-
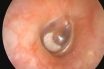
Myringosclerosis
Also known as tympanosclerosis or intratympanic tympanosclerosis, is a condition caused by calcification of collagen tissues in the tympanic membrane of the middle ear.
-
Myotonia dystrophica
An inherited disorder of the muscles and other body systems characterized by progressive muscle weakness, prolonged muscle contractions (myotonia), clouding of the lens of the eye (cataracts), cardiac abnormalities, balding, and infertility. A hereditary disease characterized by muscular wasting, myotonia, and cataract.
-
Myosarcoma
A malignant tumour containing unstriated muscle. Combined myoma and sarcoma. Malignant tumor of muscle tissue. A malignant tumor derived from myogenic cells.
-
Myopia
Near – or short-sightedness. Nearsightedness. The image theoretically falls in front of the retina of the eye because the axis of the eye is too long or the refractive power of the lens of the eye is too strong, hyperopia. A condition in which someone can see clearly objects which are close, but not ones…
-
Myocardial ischemia
An intermediate condition in coronary artery disease during which the heart tissue is slowly or suddenly starved of oxygen and other nutrients. A disorder of cardiac function caused by insufficient blood flow to the muscle tissue of the heart. The decreased blood flow may be due to narrowing of the coronary arteries (coronary arteriosclerosis), to…
-
Myocardial infarction
Is the rapid development of myocardial necrosis caused by a critical imbalance between oxygen supply and demand of the myocardium. Gross necrosis of the myocardium as a result of interruption of the blood supply to the area; it is almost always caused by atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, upon which coronary thrombosis is usually superimposed.…
-
Myocardial
Relating to heart muscles tissues. Referring to the middle and the thickest layer of the heart wall, composed of cardiac muscles. Referring to the myocardium.
Got any book recommendations?