Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
ORAC (Oxygen radical absorbance capacity)
A method of measuring antioxidant capacities in biological samples.
-
Optic placode
An ectodermal placode from which the lens of the embryonic eye develops; also called lens placode.
-
Opioid receptors
A group of G-protein coupled receptors located in the brain and various organs that bind opiates or opioid substances. Receptors located in the brain and spinal cord, as well the intestinal tract, that bind with endogenous opioids (endorphins) and opiate drugs. There are four major opioid receptor types—mu (μ), delta (δ), kappa (κ) and nociceptin…
-
Opiate
Drug derived from the opium plant. Any chemical derived from opium; it relieves pain and produces a sense of well-being. Narcotic pain relievers, such as morphine. A sedative which is prepared from opium, e.g. morphine or codeine. Drugs produced from the opium poppy. Drug that contains opium, is derived from opium, or is produced synthetically…
-
Ophthalmia (Sympathetic)
Inflammation of both eyes following trauma to one eye.
-
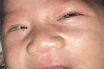
Ophthalmia
Severe inflammation of eye, or the conjunctiva or deeper structures of the eye. Also called ophthalmitis. Inflammation of the eyeball or the conjunctiva of the eye. Severe inflammation of the eye, usually including the conjunctiva. Ophthalmia, commonly known as trachoma, refers to a severe inflammation of the eye, primarily affecting the conjunctiva. In some instances,…
-
Omega 9 fatty acids
Are not essential polyunsaturated fatty acids that have in common a final carbon–carbon double bond in the n − 9 position. Some n − 9s are common components of animal fat and vegetable oil. Two n − 9 fatty acids important in industry are: oleic acid (18:1, n − 9), which is a main component…
-
Omega 6 fatty acids
Are essential polyunsaturated fatty acids that have in common a final carbon–carbon double bond in the n − 6 position. Omega-6 fatty acids are considered essential fatty acids (EFAs) found in vegetable oils, nuts and seeds. They are essential to human health but cannot be made in the body. Omega-6 fatty acids – found in…
-
Omega 3 fatty acids
Are essential polyunsaturated fatty acids that have in common a final carbon–carbon double bond in the n − 3 position. Dietary sources of omega-3 fatty acids include fish oil and certain plant/nut oils. The three most nutritionally important omega 3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Research indicates that…
-
Oliguria
Decreased production of urine. Diminished urine secretion in relation to fluid intake. A deficiency in the excretion of urine. Reduced urine secretion. Too little output of urine. A condition in which a person does not produce enough urine. Production of an abnormally small amount of urine; it may be due to kidney disease, urinary tract…
Got any book recommendations?