Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine [5-HT])
A monoamine neurotransmitter synthesized in serotonergic neurons in the central nervous system. An inhibitory neurotransmitter that figures prominently in mood and emotion. A monoamine neurotransmitter that, when decreased or deficient in the central nervous system (CNS), may lead to depression and anxiety.
-
Serotonergic
Liberating, activated by, or involving serotonin in the transmission of nerve impulses. Referring to the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine [5-ht]).
-
Serine proteinase
Peptide hydrolases which have an active centre histidine and serine involved in the catalytic process.
-
Sequela
An abnormal pathological condition resulting from a disease, injury or trauma. A disease or disorder that is caused by a disease or injury which the person had previously. Sequelae, abnormality following or resulting from a disease, injury, or treatment (e.g., paralysis following poliomyelitis). A condition resulting from a previous disease or disorder; plural is sequelae.…
-
Sensorineural bradyacuasia
Hearing impairment of the inner ear resulting from damage to the sensory hair cells or to the nerves that supply the inner ear.
-
Selenium
A trace mineral that is essential to good health but required only in tiny amounts; it is incorporated into proteins to make selenoproteins, which are important antioxidant enzymes. It is found in avocado, brazil nut, lentils, sunflower seeds, tomato, whole grain cereals, seaweed, seafood and meat. An element with the atomic symbol Se, atomic number…
-
Seizure
The physical findings or changes in behavior that occur after an episode of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. A sudden misfire among nerve cells in the brain that impairs normal brain function. Seizures are the most common symptom of epilepsy. Petite mal and grand mal seizure. A fit, convulsion or sudden contraction of the…
-
Secretagogue
A substance that causes another substance to be secreted. Causing secretion. A substance that stimulates secretion. An example is pentagastrin, which stimulates the secretion of gastric juice. That which stimulates secreting organs. Any substance that encourages the production of glandular secretions.
-

Scurf
Abnormal skin condition in which small flakes or sales become detached. Small scales on the epidermis. Dandruff-like superficial scales. A branny desquamation of the epidermis, especially on the scalp.
-
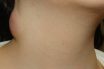
Scrofula
A tuberculous infection of the skin on the neck caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Primary tuberculosis of the cervical lymph nodes; the inflamed structures being subject to a cheesy degeneration. A tuberculous condition of the lymphatic glands characterized by enlarged suppurating abscess and cheese-like degeneration. A form of tuberculosis in the lymph nodes in…
Got any book recommendations?