Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
T-cell
A type of white blood cell that attacks virus-infected cells, foreign cells and cancer cells. Thymus derived lymphocytes or thymocytes. Comprise Thl and Th2 lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells. Thl lymphocytes are important in cell-mediated immunity and IL-2 and IFN-y production. Th2 lymphocytes are associated with the promotion of antibody-mediated immunity and production of…
-
Taeniacide
An agent that kills tapeworms. A substance which kills tapeworms.
-
Taenia
A parasitic tapeworm or flatworm of the genus, Taenia. A long ribbon-like part of the body. A large tapeworm of the genus Taenia. Genus of large parasitic tapeworms, many of which are among the most common parasites affecting humans. Included are the beef tapeworm (T. saginata) and the pork tapeworm (T. solium). A genus of…
-
Tachypnea
Abnormally rapid breathing, a common symptom in respiratory distress syndrome or persistent fetal circulation but sometimes a temporary symptom in otherwise normal infants. Abnormally fast, deep breathing. Tachypnea can upset the balance of gases in the blood by decreasing the levels of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream. Tachypnea can be a symptom of many diseases…
-
Tachyphylaxia
A decreased response to a medicine given over a period of time so that larger doses are required to produce the same response.
-
Tachycardia
A false heart rate applied to adults to rates over 100 beats per minute. Excessive rapidity in the action of the heart, usually with a heart rate above 100 beats per minute. An abnormally rapid or high heart rate. Rapid heartbeat, as occurs after exercise; may also occur, without undue exertion, as a result of…
-
Tachyarrhythmia
Any disturbance of the heart rhythm in which the heart rate is abnormally increased. A fast irregular heartbeat. Any cardiac rhythm disturbance in which the heart rate exceeds 100 beats per minute (bpm).
-
Systolic
The blood pressure when the heart is contracting. It is specifically the maximum arterial pressure during contraction of the left ventricle of the heart. The measurement of arterial blood pressure at the point of heart contraction (greatest pressure); the higher of the two BP numbers, with diastolic being the lower. Referring to the systole. The…
-
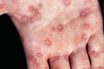
Syphilis
Is perhaps the best known of all the STD’s. Syphilis is transmitted by direct contact with infection sores, called chancres, syphilitic skin rashes, or mucous patches on the tongue and mouth during kissing, necking, petting, or sexual intercourse. It can also be transmitted from a pregnant woman to a fetus after the fourth month of…
-
Synoviocyte
Located in the synovial membrane, there are two types. Type A cells are more numerous, have phagocytic characteristics and produce degradative enzymes. Type B cells produce synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint and nurtures nourishes the articular cartilage.
Got any book recommendations?