Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-

Trachoma
A contagious disease of the conjunctiva and cornea of the eye, producing painful sensitivity to strong light and excessive tearing. A contagious disease of the conjunctiva and cornea, producing photophobia, pain, and lacrimation, caused by Chlamydia trachomatis. A contagious virus disease of the eye characterized by granular conjunctivitis. A contagious disease of the conjunctivas. It…
-
Tracheitis
Is a bacterial infection of the trachea; also known as bacterial tracheitis or acute bacterial tracheitis. Inflammation of the trachea due to an infection. Inflammation of the trachea, usually secondary to bacterial or viral infection in the nose or throat. Tracheitis causes soreness in the chest and a painful cough and is often associated with…
-
Toxemia
Is the presence of abnormal substances in the blood, but the term is also used for a serious condition in pregnancy that involves hypertension and proteinuria. Also called preeclampsia. Condition in which poisonous products of body cells at a local source of infection or derived from the growth of microorganisms are spread throughout the body…
-
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
Is a method of feeding that bypasses the gastrointestinal tract. Total parenteral nutrition. A method of providing all nutrients needed through a solution infused into a large blood vessel. Administration of a nutritionally adequate solution (containing, e.g., proteins, electrolytes, and vitamins) through a catheter into the vena cava; used to provide nutrients in cases of…
-
Topoisomerases
A class of enzymes involved in the regulation of DNA supercoiling. One of several enzymes that cleave and rejoin the coiled sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA or RNA.
-
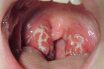
Tonsillitis
An inflammatory condition of the tonsils due to bacteria, allergies or respiratory problems. Inflammation or infection of a tonsil, especially the palatine tonsils. Acute tonsillitis, often caused by bacterial, especially streptococcal, infection, produces sore throat, fever, headache, enlarged lymph glands in the neck region, and difficulty in swallowing. Treatment is by rest, fluids, and antibiotics.…
-
Tonic clonic seizure
A type of generalized seizure that affects the entire brain. Previously referred to as grand mal, this seizure variety involves a loss of consciousness accompanied by muscular rigidity and subsequent involuntary jerking motions. Typically lasting just a brief duration, these seizures can become life-threatening if they extend into prolonged tonic-clonic episodes.
-
Tonic
Substance that acts to restore, balance, tone, strengthen, or invigorate a body system without overt stimulation or depression. Exerts a restorative or stimulant action on the body. Substance taken to strengthen the body or a particular system of the body, generally in the treatment of chronic disease. Loosely, a tonic “tones” whatever system it affects.…
-
Toll-like receptors (TLRs)
Are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. One of several receptors on macrophages and other immune and endothelial cells that recognizes pathogen components such as peptidoglycan or lipopolysaccharide. Activation of a receptor stimulates release of cytokines and other chemical signals that are part of innate immunity.
-
Tocotrienol
Fat soluble organic compounds belonging to vitamin E group.
Got any book recommendations?