Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
Yellow fever
Is a viral disease that is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes. Illness ranges in severity from an influenza-like syndrome to severe hepatitis and hemorrhagic fever. Yellow fever virus (YFV) is maintained in nature by mosquitoborne transmission between nonhuman primates. A tropical epidemic disease caused by mosquito-borne viral infection. A viral disease…
-
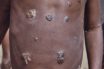
Yaws
An infectious tropical infection of the skin, bones and joints caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pertenue, characterized by papules and pappiloma with subsequent deformation of the skins, bone and joints; also called framboesia. An infectious, nonvenereal tropical disease caused by Treponema pertenus. It is characterized by an initial lesion (the motheryaw), followed by further…
-
Xerophthalmia
A medical condition in which the eye fails to produce tears. Advanced vitamin A deficiency in which the epithelium of the cornea and conjunctiva of the eye deteriorate because of impairment of the tear glands, resulting in dryness then ulceration, leading to blindness. Excessive dryness of the conjunctiva. A condition of the eye, in which…
-
Xenobiotics
A chemical (as a drug, pesticide, or carcinogen) that is foreign to a living organism. Substances foreign to the body, including drugs and some food additives. An antibiotic not produced by the body, and thus foreign to it.
-
Xanthones
Unique class of biologically active phenol compounds with the molecular formula C13H8O2 possessing antioxidant properties, discovered in the mangosteen fruit.
-
Xanthine oxidase
A flavoprotein enzyme containing a molybdenum cofactor (Moco) and (Fe2S2) clusters, involved in purine metabolism. In humans, inhibition of xanthine oxidase reduces the production of uric acid, and prevent hyperuricemia and gout. An enzyme responsible for production of free radicals in the body.
-
X-linked agammaglobulinemia
Also known as X-linked hypogammaglobulinemia, XLA, Bruton type agammaglobulinemia, Bruton syndrome, or sex-linked agammaglobulinemia; a rare x-linked genetic disorder that affects the body’s ability to fight infection.
-

Whooping cough
Acute infectious disease usually in children caused by a Bacillus bacterium and accompanied by catarrh of the respiratory passages and repeated bouts of coughing. A respiratory infection caused by Bordetella pertussis and characterized by paroxysmal coughing ending in a prolonged crowing intake of breath. A bacterial infection especially of the children caused by bacterium Bordetella…
-
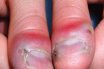
Whitlow
Painful infection of the hand involving one or more fingers that typically affects the terminal phalanx. An infection of the fingers caused by herpes simplex virus. An old general term for any suppurative inflammation on a finger or toe. An inflammation caused by infection near the nail in the fleshy part of the tip of…
-
White fat
White adipose tissue (WAT) in mammals, store of energy. cf. brown fat.
Got any book recommendations?