Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
Blastomere
Any of the cells formed from the first few cleavages in animal embryology. Any of the cells produced by cleavage of the zygote, comprising the earliest stages of embryonic development until the formation of the blastocyst. Blastomeres divide repeatedly without growth and so decrease in size. One of the cells resulting from the cleavage of…
-
Blastoderm
A membrane formed by the repeated segmentation of the blastomeres. A disk of cells (germinal disk or blastodisk) that develops on the surface of the yolk in an avian or reptilian egg from which the embryo develops; also, in mammalian embryos a disk of cells lying between the yolk sac and the amniotic cavity from…
-
Blastocyte
The cell mass that forms from the morula and is implanted in the uterus during the first week of pregnancy.
-
Blastocoele
The hollow segmentation cavity of the blastula. A cavity filled with fluid in a morula. The fluid-filled cavity that develops within the blastocyst. The cavity increases the surface area of the embryo and thus improves its ability to absorb nutrients and oxygen. The cavity in the blastula of the developing embryo.
-
Blackwater fever
A fatal infectious malarial fever characterized by destruction of the red blood cells, hemoglobinuria. A form of malaria where haemoglobin from red blood cells is released into plasma and makes the urine dark. A rare and serious complication of malignant tertian (falciparum) malaria in which there is massive destruction of the red blood cells, leading…
-
Blackout
Temporary loss of memory. To have sudden loss of consciousness. A temporary loss of consciousness or vision. When a blackout occurs, a doctor should be consulted to determine the cause. A period of time that a person who has been drinking cannot recall. Brief loss of consciousness and vision impairment caused by reduced blood flow…
-
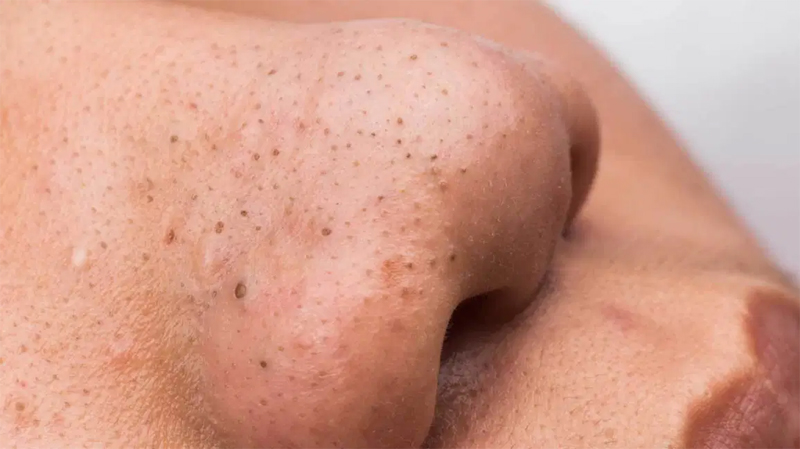
Blackhead
A comedone. A pimple that has darkened at the top due to exposure to the air. Blackheads typically develop as the plug of greasy material (keratin) blocking a sebaceous gland is exposed over time to oxygen in the air. Blackheads are often a characteristic of acne and usually appear on the face, chest, shoulders, and…
-
Black death
Bubonic plague. The medieval term for bubonic plague, a devastating disease that claimed the lives of approximately 50 percent of its victims during past epidemics, was “Black Death.” This name stemmed from a notable characteristic of the illness, which involved bleeding beneath the skin, leading to the formation of bluish-black bruises. The term “Black Death”…
-
Bivalent chromosomes
Two chromosomes, one from the male and the other from the female, united temporarily. A double chromosome resulting from the conjugation of two homologous chromosomes in synapsis, which occurs during the first meiotic division.
-
Bivalent
In genetics, a pair of synapsed or associated homologous chromosomes which may or may not have undergone the duplication process to form a group of four chromatids. A structure consisting of homologous chromosomes attached to each other by chiasmata during the first division of meiosis. In chemistry, having an valence of two.
Got any book recommendations?