Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
Earache
Pain in the ear; it may be caused by ear disease or by infection or disease of the nose, mouth region, throat, and other nearby areas; also called otalgia. Pain in one or both ears, medically termed otalgia, which may be sharp and stabbing or dull and throbbing. When earaches are severe and persistent, an…
-
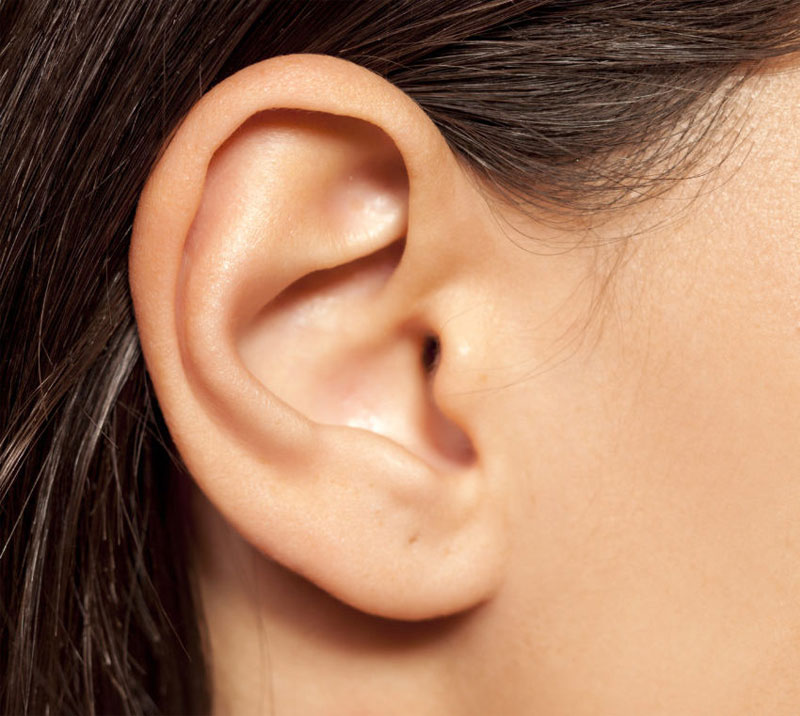
Ear
Hearing and balance organ, including three general structures; the outer (external) ear; the middle ear, including the eardrum cavity and the three tiny bones that transmit the hearing vibrations; and the inner (internal) ear, including the main organ of hearing (the organ of Corti) and the balance mechanism. The organ for hearing and balance. The…
-
Dysautonomia
Rare hereditary disease resulting in autonomic nervous system dysfunction, most commonly m Ashkenazi Jews. Symptoms include mental retardation, lack of coordination, vomiting, frequent infections, and seizures. A rare hereditary disease involving the autonomic nervous system and characterized by mental retardation, motor incoordination, vomiting, frequent infections, and convulsions. It is seen almost exclusively in Ashkenazi Jews.…
-
Drosophilia
Type of fly, including the common fruit fly. Substance taken by mouth, injection, or applied locally to prevent or treat a disorder (e.g., to ease pain).
-
Doxazosin
Oral antihypertensive agent, administered once daily; the most common side effect is orthostatic hypotension. A drug that lowers high blood pressure. Doxazosin (Cardura) dilates arteries and veins and is used to treat high blood pressure and other conditions, such as a benign enlarged prostate. It also lowers cholesterol levels. Doxazosin belongs to a class of…
-
Double pneumonia
Pneumonia of both lungs at the same time. Pneumonia that involves both lungs or two lobes.
-
Donnatal
Fixed-combination drug, containing a sedative (phenobarbital) and several other agents, used to decrease gastrointestinal spasm.
-
Dissolution
Breakup in the normal anatomical state of part or parts of an organism. Rate at which a drug becomes a solution. The disintegration of a body into its constituent parts; conversion into a liquid state; an approaching state of death.
-
Dipole
Molecule in which each end has an equal, but opposite, electrical charge; may also refer to oppositely charged poles of a magnet. A molecule in which each end has an equal but opposite charge. The intensity of the charge is given by its dielectric moment or constant.
-
Diliution
Decrease in the amount of a substance in a solution for each unit of volume, usually the result of adding water to increase the volume.
Got any book recommendations?