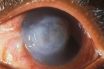
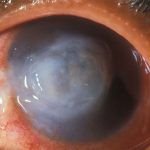
 An eye disorder that leads to a dry cornea.
An eye disorder that leads to a dry cornea.
Progressive softening and ulceration of the cornea, due to vitamin A deficiency. Blindness is usually inevitable unless the deficiency is corrected at an early stage.
An affliction of the cornea characterized by dryness with ulceration and perforation resulting from vitamin A deficiency.
A softening of the cornea frequently caused by Vitamin A deficiency.
Softening of the horny layer of the skin.
Destruction of the cornea of the eye and consequent blindness as a result of severe vitamin A deficiency.
Softening, drying, and ulceration of the cornea, usually resulting from severe vitamin A deficiency in the diet or from a disease that impairs vitamin A absorption or storage in the body (e.g., cystic fibrosis; sprue).
A progressive disease of the eye due to vitamin A deficiency. The cornea softens and may become perforated. This condition is very serious and blindness is usually inevitable.
Softening of the cornea seen in early childhood owing to deficiencies of vitamin A.
A gradual eye ailment triggered by severe deficiency in vitamin A, resulting in the cornea (the clear front portion of the eyeball) becoming cloudy and developing ulcers. Corneal perforation is frequently observed, which can lead to eye loss due to infection. Typically, this condition is prevalent in significantly malnourished children and stands as a prevalent cause of blindness in developing nations.
During the initial phases, substantial doses of vitamin A can potentially reverse the damage. However, if the condition is disregarded and left untreated, blindness is typically an unavoidable outcome.
The cornea of the eye becoming less firm because of a lack of vitamin A in the diet.