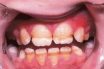
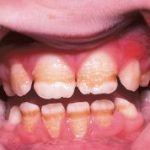
 In dentistry, the hard, thin, translucent layer of calcified material that covers the coronal portion of a tooth. It protects the dentin located directly underneath it and is known to be the hardest substance in the body. Called also adamantine layer.
In dentistry, the hard, thin, translucent layer of calcified material that covers the coronal portion of a tooth. It protects the dentin located directly underneath it and is known to be the hardest substance in the body. Called also adamantine layer.
A very hard whitish substance which covers the dentine of the anatomical crown of a tooth.
Mineralised tissue that forms hard outer surface of tooth.
In dentistry, the outer covering of the crown of the tooth, which is an extremely hard tissue.
The hard white shiny outer covering of the crown of a tooth.
The hard glistening substance covering the crown of the tooth.
The hard material that covers the crown of the tooth; can be worn away as a result of frequent vomiting.
Hard white covering above the gum line of a tooth.
The insensitive and extremely hard outer covering of the crown of a tooth, consisting of white calcified tissue produced by cells (ameloblasts) of the enamel organ.
The hard, white, dense, inorganic substance covering the crown of the teeth. Enamel is composed of hydroxyapatite crystal, a calcium-containing salt. The crystals are arranged to form a rod. The enamel rods are organized to form the enamel. Enamel is the hardest substance in the body. Demineralization may result in a carious lesion, or “cavity.”