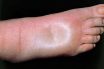
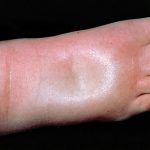
 A condition of abnormally large fluid volume or abnormal swelling subsequent to the collection of fluid in a tissue or part.
A condition of abnormally large fluid volume or abnormal swelling subsequent to the collection of fluid in a tissue or part.
Formerly known as dropsy or hydropsy, is characterized swelling caused by abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin, or in one or more cavities of the body. It usually occurs in the feet, ankles and legs, but it can involve the entire body.
An abnormal accumulation of fluid in body parts or tissues; swelling.
A localized or systemic condition in which the body tissues contain an excessive amount of fluid. Systemic edema can be as mild as premenstrual water retention (I mean mild by comparison) or involve loss of blood proteins or kidney and heart failures. Local edema is the result of extensive or extended inflammation, with blood protein leakage and the loss of interstitial colloid.
A painless swelling caused by fluid retention beneath the skills surface.
Excessive accumulation of fluid in bodily tissues. May be localized or general.
Accumulation of water in the tissues.
Retention of fluids within the body, causing swelling.
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the body’s tissues, causing swelling; a sign of imbalances and disruptions of the body’s chemistry that can result from a wide variety of diseases and disorders, such as kidney and urological disorders or eclampsia. Drugs called diuretics are often prescribed, and salt is restricted in the diet to lessen fluid retention.
Abnormal collection of fluid in spaces between cells, esp. just under the skin or in a given cavity (e.g., peritoneal cavity) or organ (e.g., the lungs pulmonary edema). Causes include injury, heart disease, kidney failure, cirrhosis, and allergy. Treatment depends on the cause but often involves bedrest, diuretics, and restriction of salt. Formerly known as dropsy; also called hydrops.
Excessive accumulation of fluid in body tissues accompanied by swelling.
Swelling in the body caused by a buildup of excess fluids. Edema can occur when increased pressure in the blood vessels disturbs the fluid exchange and forces more fluid out of the blood vessels and into the surrounding tissues. Edema can occur in different parts of the body and for various reasons, some of which are minor and others serious. A serious cause of edema is congestive heart failure, which can cause persistent swelling in the lower extremities and fluid buildup in the lungs. However, most cases of leg swelling are not serious, and the most common cause is increased pressure in the leg veins from damaged valves in the veins.
Excessive accumulation of fluid in the body tissues: popularly known as dropsy. The resultant swelling may be local, as with an injury or inflammation, or more general, as in heart or kidney failure In generalized edema there may be collections of fluid within the chest cavity (pleural effusions), abdomen, or within the air spaces of the lung (pulmonary edema). It may result from heart on kidney failure, cirrhosis of the liver, acute nephritis, the nephrotic syndrome, starvation, allergy, or drugs (e.g. phenylbutazone or cortisone derivatives). In such cases the kidneys can usually be stimulated to get rid of the excess fluid by the administration of ‘diuretic drugs. Subcutaneous edema commonly occurs in the legs and ankles due to the influence of gravity and (in women) before menstruation; the swelling subsides with rest and elevation of the legs.
A local or generalized condition in which body tissues contain an excessive amount of tissue fluid in the interstitial spaces. Ascites and hydrothorax and pericardial effusion are words for third spacing of excess fluid in the peritoneal and pleural cavities and the pericardium, respectively. Generalized edema was previously termed dropsy; it is now known as anasarca.
The abnormal pooling of fluid in tissues that can be caused by conditions such as congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, draining wounds, excessive bleeding, and malnutrition.
The distension of anatomical structures due to the gathering of aqueous substance in the intercellular compartment.
The unusual buildup of fluid within bodily tissues.
The condition of having unusually high amounts of fluid in the body’s intercellular tissue spaces, often evident as an excessive accumulation of fluid in the subcutaneous tissues. Edema can be localized due to venous or lymphatic blockage or increased vascular permeability, or it can be systemic, resulting from heart failure or kidney disease.