 Paralysis of the ciliary muscle which makes it impossible for the eye to focus properly.
Paralysis of the ciliary muscle which makes it impossible for the eye to focus properly.
Loss of functionality of the ciliary muscle of the eye due to denervation or medication.
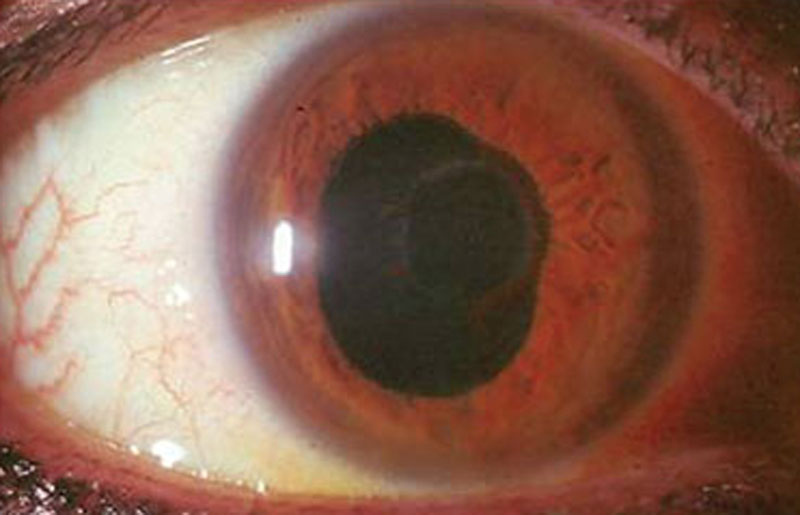
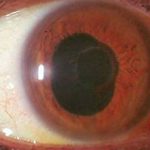
Paralysis of the ciliary muscles surrounding the lens of the eye. Since these muscles are central to reshaping the lens for focusing on near objects, the eye loses its ability to focus on objects close to the eye. Drops that dilate the eye often cause temporary cycloplegia.
Paralysis of the ciliary muscle of the EYE, which results in the loss of the power of accommodation in the eye.
Paralysis of the ciliary muscle. This can be an anticholinergic side effect of antipsychotic or antidepressant medications.
The impairment of the ciliary muscle in the eye results in a condition known as cycloplegia, which hinders the eye’s ability to accommodate. In certain situations, the administration of cycloplegic medications may deliberately induce cycloplegia to facilitate thorough eye examinations. This method proves valuable in ensuring accurate and comprehensive assessments of ocular health.
The loss of the ability to change focus due to the paralysis of the ciliary muscles in the eye.