 A thin, acellular, organic structure overlying the enamel surface; proteinaceous, and may contain tissue components.
A thin, acellular, organic structure overlying the enamel surface; proteinaceous, and may contain tissue components.
A thin protective layer over the surface of a plant.
Layer on the outer walls of the epidermis composed of cutin, a fatty, water-repellent material.
Outer waxy layer on the epidermis composed of a fatty water-repellent substance.
A varnish-like layer covering the epidermis.
The outer layer of your hair shaft, the bit you see.
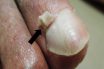
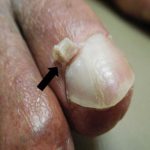
Layer of skin at the base of the nail.
The outer epidermal layer of cells in grains and seeds. Also the red skin present on groundnut kernels.
A layer of solid or semisolid tissue that covers the free surface of a layer of epithelial cells. It may be horny or chitinous and sometimes is calcified. Examples include the enamel cuticle of a tooth and the capsule of the lens of the eye.
The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin. This term is commonly used to describe the thin flap of skin located at the base of a nail, known as the cuticle. Additionally, it refers to the outer layer of a hair shaft, which plays a protective role in safeguarding the hair strand. The epidermis serves as a barrier, shielding the body against external elements, regulating moisture levels, and contributing to the overall health and integrity of the skin and hair.
The delicate skin layer that covers the nail’s base.