 Destruction of tissue by extreme cold. Usually achieved with liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide.
Destruction of tissue by extreme cold. Usually achieved with liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide.
Destruction of diseased or unwanted tissues by freezing.
Surgery which uses extremely cold instruments to destroy tissue.
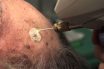
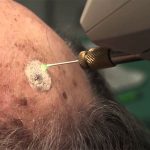
Use of extreme cold (e.g., liquid nitrogen) to destroy unwanted tissue (e.g., warts, cataracts, skin cancer). The cooling agent is applied by means of a metal probe; temperatures as low as — 160°C can be achieved.
Localized freezing of diseased tissues for surgical removal.
A surgical process using a very cold (refrigerated) probe to remove or destroy tissue.
Using a temperature below freezing to remove abnormal or diseased tissue. Cryosurgery is used to remove lesions, such as warts, from the skin and to treat cancer or precancerous conditions of the cervix. The freezing agent used is typically liquid nitrogen, which has a temperature of approximately-256°F. Depending on the location of the abnormal tissue, the nitrogen can be applied with a cotton-tipped applicator or a metal probe.
The use of extreme cold in a localized part of the body to freeze and destroy unwanted tissues. Cryosurgery is usually undertaken with an instrument, a cryoprobe, which has a fine tip cooled by allowing carbon dioxide or nitrous oxide gas to expand within it. Cryosurgery is commonly used for the removal of cataracts and the destruction of certain bone tumors.
The use of cold in surgery. Its advantages include little associated pain, little or no bleeding, and excellent healing with little or no scar formation. Hence its relatively wide use in eye surgery, some abdominal surgery, skin cancers and haemorrhoid treatment. The coolants used include liquid nitrogen with which temperatures as low as -196 °C can be obtained, carbon dioxide (-78 °C) and nitrous oxide (-88 °C).
The use of extremely cold probes to destroy unwanted, cancerous, or infected tissues. Cryosurgery has been used to treat a variety of lesions, including metastatic liver cancer, prostate cancer, sun-induced skin cancers, warts, cutaneous leishmaniasis, and even abnormal conduction pathways in the heart or nervous system. Liquid nitrogen is often used to produce the extreme cold.
Cryosurgery refers to the utilization of sub-freezing temperatures to eliminate tissue, or the application of cold during surgical interventions to create adhesion between a medical instrument and a specific area of bodily tissue.
Cryosurgery yields minimal scarring and finds application in the treatment of malignant tumors located in areas where extensive scarring could obstruct vital passages, such as the cervix, liver, and intestines. Moreover, it is employed in ophthalmic procedures like cataract surgery and the management of retinal detachment. Furthermore, cryosurgery is commonly utilized for the removal of warts, skin tags, certain birthmarks, specific types of skin cancers, as well as the treatment of hemorrhoids.
The elimination of tissue through the application of intense cold, such as in treating specific cancerous skin lesions and alleviating tremors in Parkinson’s disease by targeting particular regions of the thalamus.