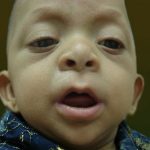
 A type of intellectual disability and bodily malformation caused by severe, uncorrected thyroid deficiency in infancy and early childhood.
A type of intellectual disability and bodily malformation caused by severe, uncorrected thyroid deficiency in infancy and early childhood.
Underactivity of the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism) in children, resulting in poor growth, severe mental retardation and deafness.
A condition caused by thyroid malfunction typically includes feeble mindedness.
A disease in children which results from too little thyroxine production by the thyroid gland. It is characterized by poor growth and development and mental retardation.
Cretinism is a syndrome caused by hypothyroidism (underactivity of the thyroid gland) at birth. Two types of cretinism have been distinguished. Endemic cretinism is essentially an iodine deficiency disorder. Insufficient levels of iodine cause maternal hypothyroidism, which increases the incidence of fetal hypothyroidism in the neonate. Endemic cretinism is characterized by severe developmental delays, deaf-mutism, and spasticity of the arms and legs. The second form, sporadic cretinism or congenital hypothyroidism, is most commonly caused by a developmental defect of the thyroid gland, in which the thyroid gland fails to develop (aplasia) or is underdeveloped (hypoplasia; Vanderbilt University Medical Center, 1998). Developmental delays and stunted growth are the most common complications associated with sporadic cretinism.
A congenital syndrome of mental retardation, decreased metabolism, and impaired physical development secondary to insufficient production of thyroid hormones.
Severe, congenital hypothyroidism characterized by dwarfism, mental retardation, coarse dry skin and features, and muscular incoordination. It results from thyroid deficiency or inadequate iodine intake by the mother while the fetus is developing. Relatively rare in the United States, the disorder occurs mainly in areas where the diet lacks sufficient iodine and goiter is prevalent.
Congenital hypothyroidism that can cause mental retardation if left untreated.
A syndrome of dwarfism, mental retardation, and coarseness of the skin and facial features due to lack of thyroid hormone from birth (congenital hypothyroidism).
An out-of-date name for congenital hypothyroidism, a disease caused by defective thyroid function in fetal life or early in infancy.
A congenital condition caused by a lack of thyroid hormones, characterized by arrested physical and mental development, myxedema, dystrophy of the bones and soft tissues, and lowered basal metabolism. The treatment consists of administration of synthetic thyroid hormones. The acquired form of severe hypothyroidism is referred to as myxedema.
This is a medical condition marked by a constellation of symptoms that include cognitive impairment, hearing loss, and stunted growth, all stemming from a deficit in the production of thyroid hormone.
At the time of birth, a profound form of hypothyroidism may manifest, displaying severe intellectual disability as its defining trait.
Cretinism, a congenital disorder observed in infants, manifests as impaired growth, developmental delays, learning challenges, and distinctive facial features. This condition arises when the thyroid gland fails to produce adequate levels of thyroxine, the essential thyroid hormone, during birth. Nonetheless, if identified early, the administration of thyroxine replacement therapy can lead to a complete recovery.
A condition observed in newborn infants resulting from an underactive thyroid gland. This disorder leads to stunted growth, along with impaired mental and sexual development. Physical characteristics include coarse and broad facial features, a swollen tongue, and other symptoms associated with myxedema. This condition can be effectively treated with doses of dried thyroid gland. Cretinism tends to occur in regions where goiter is prevalent among adults, although adult goiter does not necessarily result in cognitive decline, unlike cretinism, which often leads to severe intellectual impairment. It is believed that cretinism and myxedema are linked to insufficient dietary iodine intake in regions where these conditions are prevalent, and many countries have addressed this issue by adding iodine to table salt. Cretinism is also referred to as congenital myxedema.
