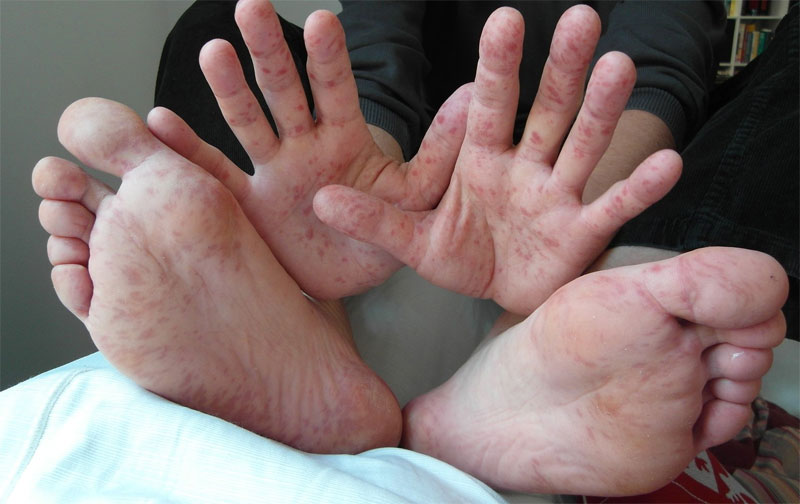
 One of a group of enteroviruses which enter the cells of the intestines and can cause diseases such as aseptic meningitis and Bornholm disease [After Coxsackie, New York, where the virus was first identified].
One of a group of enteroviruses which enter the cells of the intestines and can cause diseases such as aseptic meningitis and Bornholm disease [After Coxsackie, New York, where the virus was first identified].
One of a group of RNA containing viruses that are able to multiply in the gastrointestinal tract. About 30 different types exist. Type A Coxsackie viruses generally cause less severe and less well-defined diseases, although some cause meningitis and severe throat infections (see herpangina). Type B Coxsackie viruses cause inflammation or degeneration of brain, skeletal muscle, or heart tissue