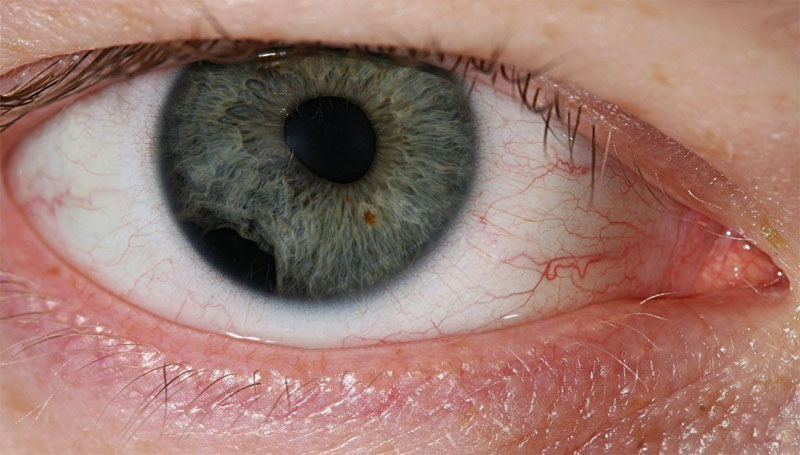
 A scratch on the cornea, caused by something sharp getting into the eye.
A scratch on the cornea, caused by something sharp getting into the eye.
Loss of or damage to superficial layers of the cornea due to trauma or repetitive irritation, such as a foreign particle under a contact lens.
An injury to the thin skin (epithelium) overlying the transparent covering (cornea) of the eye. Symptoms may include severe pain in the eye, sensation of a foreign body in the eye, abnormal vision, sensitivity to light, redness, and swollen eyelids. Treatment consists of removing any foreign body that may be present, lubrication with artificial tears or ointment, and antibiotic drops or ointment in the eye if infection poses a risk. Most doctors recommend covering the eye with a patch to allow healing and relief of pain. Corneal injuries heal quickly with treatment and the eye typically returns to normal within 24 to 48 hours.
A corneal abrasion refers to a scratch or damage to the outer layer of the cornea, known as the epithelium, typically caused by a small, sharp object entering the eye or as a result of an injury. While corneal abrasions generally heal rapidly, they can induce intense pain and sensitivity to light, known as photophobia.
The treatment for a corneal abrasion involves applying a patch to cover the affected eye and administering analgesics to alleviate pain. If the ciliary muscles experience spasms, eye drops containing cycloplegic drugs may be utilized to temporarily paralyze these muscles. Additionally, antibiotic eye drops are commonly prescribed to prevent bacterial infections that could potentially lead to the formation of a corneal ulcer.