Category: X
-
Xylose absorption test
A test done to determine the rate of absorption of xylose, a wood sugar, into blood. Absorption is impaired in certain disorders of fat absorption.
-
Xyphoid process
The small tip at the inferior end of the sternum.
-
X-Iinked
To genes, characteristics, or conditions carried on the X chromosome.
-
Xeroma
Abnormally dry condition of the conjunctiva of the eye.
-
Xanthosarcoma
Malignant neoplasm of tendon sheaths and aponeuroses, containing xanthoma cells. A harmful condition that affects the fibrous tissue coverings of organs and muscles, as well as tendon sheaths, is known as xanthomyeloma. This disease targets the fascial planes, which are the layers of connective tissue surrounding these structures.
-
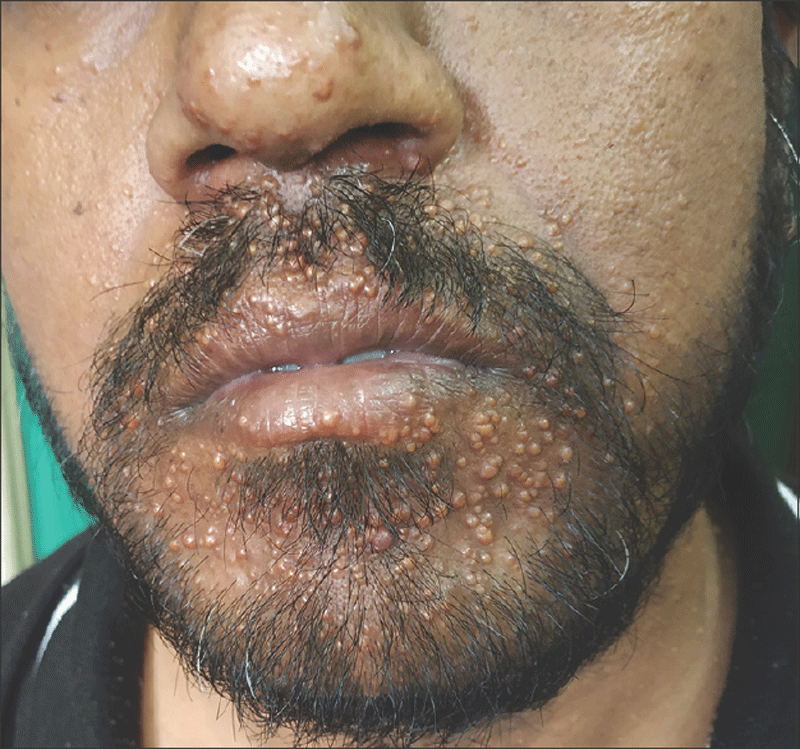
Xanthoma disseminatum
Chronic condition in which orange or brownish papules develop on many surfaces of the body, especially in the region of the mouth, in the upper respiratory tract, and on skin folds. A condition characterized by the presence of xanthomata throughout the body, especially on the face, in tendon sheaths, and in mucous membranes.
-
XXX syndrome
XXX syndrome is a disorder in which affected females have three X chromosomes. It may also be referred to as Chromosome X, Triplo-X, and Chromosome 47, XXX karyotype. XXX syndrome was first described by P. A. Jacobs in the Lancet in 1959. It is the most frequent X chromosomal anomaly in females. The incidence of…
-
Xeroderma pigmentosum
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by extreme photosensitivity of the skin and eyes. Even minimal sun exposure can result in blistering of the skin, freckling, or both. The disorder is due to a defect in the ability of the cell to repair DNA damaged by ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The deficiency is…
-
X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome
X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome (XLP) is an inherited immunodeficiency disorder characterized by one or more of three major phenotypic presentations. These presentations include a defective response to infection with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), acquired hypogammaglobulinemia, and malignant B-cell lymphoma (National Organization for Rare Disorders, 2001). Patients exhibit a range of symptoms, including life-threatening EBV infection, lymphoma…
-
X-linked hydrocephalus syndrome
X-linked hydrocephalus is one type of congenital hydrocephalus that results when circulation and absorption of the cerebrospinal fluid within the ventricles are impeded or impaired. The acronym HSAS was coined because stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius (a narrow passageway linking the third and fourth ventricles) was originally thought to be the causative agent of…