Category: S
-
Secondary stability
Implant stability within its prepared bony site, created by osseointegration and the formation of new bone subsequent to loss of the bone initially in contact with the implant at the time of placement. This delayed clinical implant immobility may follow osteotomy site augmentation with bone substitutes and/or healing adjuncts. Compare: Primary stability, secondary union.
-
Secondary occlusal trauma
The effects induced by occlusal force (normal or abnormal) acting on teeth with decreased periodontal support.
-
Secondary maxillary mucocele (syn)
Postoperative maxillary sinus cyst. Maxillary sinus lesion caused by previous trauma or surgery which divides the sinus into two compartments. The cyst is derived from the antral epithelium and mucosal remnants that were previously entrapped within the surgical site.
-
Secondary closure
Misnomer, since the general goal of surgery is to have close flap adaptation and complete closure of the surgical site, and hence healing by primary intention. However, in certain situations, incomplete closure is indicated, which leads to healing by secondary intention.
-
Second stage dental implant surgery
For eposteal dental implant surgery, the term refers to the procedure involving placement of the eposteal framework fabricated after the first stage implant surgery. For endosteal dental implant surgery, after surgical reflection, the occlusal aspect of the dental implant is exposed, the cover screw is removed, and either the interim or definitive dental implant abutment…
-
Sebaceous
Relating to or resembling fat or sebum; oily; fatty; discharging fat or a grease like oil substance. Fatty, or with the appearance of fat. Gland that secretes sebum. Containing, or to, sebum, an oily, fatty matter secreted by the sebaceous glands.
-
Sealing screw
Healing component used to cover the coronal portion of the implant or as part of a transmucosal healing component that seals the occlusal portion of that component.
-
SE (abbrev)
Standard error.
-
SD (abbrev)
Standard deviation.
-
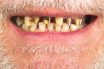
Scurvy
Malnutrition caused by a dietary deficiency of vitamin C. Oral manifestations may include ulcerations, mucosal hemorrhage, and gingival enlargement. A state of dietary deficiency of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) which is required for the synthesis of collagen in humans. Deficiency of vitamin C leading to impaired collagen synthesis, causing capillary fragility, poor wound healing and…