Category: S
-
STD
Sexually transmitted disease
-
Status epilepticus
Refers to a life-threatening condition in which the brain is in a state of persistent seizure. Continuous epileptic seizures. A condition in which one major attack of epilepsy succeeds another with little or no intermission. Repeated and prolonged epileptic seizures without recovery of consciousness between them. An emergency situation characterized by a rapid series of…
-
Statin
A type of lipid-lowering drug. A family of related drugs used to treat hypercholesterolaemia. They act by inhibiting hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA reductase (HMG CoA reductase), the first and rate-limiting enzyme of cholesterol synthesis. A lipid-lowering drug which inhibits an enzyme in cholesterol synthesis, used to treat people with, or at high risk of developing, coronary heart…
-
Stanch
To stop or check the flow of a bodily fluid like blood from a wound. To stop the flow of blood from a wound. To control or halt the flow, especially of blood.
-
Sputum
Matter coughed up and usually ejected from the mouth, including saliva, foreign material, and substances such as mucus or phlegm, from the respiratory tract. Substance expelled by coughing or clearing the throat. Mucus-based material that can be expectorated from the lungs and air passages usually results from disease of the air passages. Mucus which is…
-
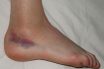
Sprain
To twist a ligament or muscle of a joint without dislocating the bone. Wrenching or twisting of a joint in which ligaments are stretched past their normal limits. A sprain is an injury to a ligament—a stretching or a tearing. One or more ligaments can be injured during a sprain. An injury to ligaments, tendons,…
-
Splenomegaly
Is an enlargement of the spleen. A condition in which the spleen is unusually large, associated with several disorders including malaria and some cancers. Enlargement of the spleen, caused by malaria, certain types of anemia, certain infectious diseases (e.g., infectious mononucleosis), and other disorders. Enlargement of the spleen, detectable with palpation of the abdomen; possible…
-
Splenocyte
Is a monocyte, one of the five major types of white blood cell, and is characteristically found in the splenic tissue. A monocyte found in the spleen or in splenic tissue. A type of white blood cell located in the spleen.
-
Splenitis
Inflammation of the spleen, usually as a result of infection.
-
Spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK)
Is an enigmatic protein tyrosine kinase functional in a number of diverse cellular processes such as the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses.