Category: S
-
Sere
A series of ecological communities formed in ecological succession.
-
Systolic
The blood pressure when the heart is contracting. It is specifically the maximum arterial pressure during contraction of the left ventricle of the heart. The measurement of arterial blood pressure at the point of heart contraction (greatest pressure); the higher of the two BP numbers, with diastolic being the lower. Referring to the systole. The…
-
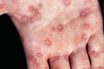
Syphilis
Is perhaps the best known of all the STD’s. Syphilis is transmitted by direct contact with infection sores, called chancres, syphilitic skin rashes, or mucous patches on the tongue and mouth during kissing, necking, petting, or sexual intercourse. It can also be transmitted from a pregnant woman to a fetus after the fourth month of…
-
Synoviocyte
Located in the synovial membrane, there are two types. Type A cells are more numerous, have phagocytic characteristics and produce degradative enzymes. Type B cells produce synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint and nurtures nourishes the articular cartilage.
-
Synovial
Lubricating fluid secreted by synovial membranes, as those of the joints. Pertaining to a lubrication fluid around a joint, bursa, and tendon sheath. Of, or pertaining to, or secreting synovia. Referring to the synovium.
-
Syngeneic
Genetically identical or closely related, so as to allow tissue transplant; immunologically compatible. Referring to individuals or tissues that have an identical or closely similar genetic make-up, especially one that will allow the transplanting of tissue without provoking an immune response. Descriptive of individuals or cells without detectable tissue incompatibility. Strains of mice that are…
-
Syneresis
Expulsion of liquid from a gel, as contraction of a blood clot and expulsion of liquid. The contraction of a gel when left standing. The releasing of fluid as in a blood clot when it becomes harder. Contraction of a blood clot. When first formed, a blood clot is a loose meshwork of fibers containing…
-
Syncope
Fainting, sudden loss of consciousness followed by the return of wakefulness. A loss of consciousness. Syncope is the medical term for fainting. Transient loss of consciousness due to inadequate blood flow to the brain. Fainting, lightheadedness. A condition in which someone becomes unconscious for a short time because of reduced flow of blood to the…
-
Sympathetic nervous system
The part of the autonomic nervous system originating in the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord that in general inhibits or opposes the physiological effects of the parasympathetic nervous system, as in tending to reduce digestive secretions or speed up the heart. The part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) that responds to…
-
SYK, Spleen tyrosine kinase
Is a human protein and gene. Syk plays a similar role in transmitting signals from a variety of cell surface receptors including CD74, Fc Receptor, and integrins.