Category: M
-
Malocclusion
Any deviation from a physiologically acceptable contact between the opposing dental arches. Any deviation from a normal occlusion. Improper alignment of the upper and lower teeth when biting. Improper positioning and faulty contact of the teeth. A dental condition characterized by the irregularity of teeth and improper alignment of the biting surfaces of the teeth.…
-
Malleable
Capable of being extended or shaped with a hammer or with the pressure of rollers. Having the property of being shaped by pressure.
-
Malignant
In the case of a neoplasm, having the properties of anaplasia, invasion, and metastasis. Cancerous; a growth with a tendency to invade and destroy nearby tissue and spread to other parts of the body. A neoplasm that is cancerous. Likely to cause death or serious disablement if not properly treated. In medicine, a general term…
-
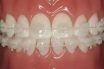
Malalignment, dental
The displacement of a tooth from its normal position in the dental arch.
-
Major (thread) diameter
The largest diameter of a screw thread. It corresponds to the diameter by which the screw is designated.
-
Major connector
The part of a partial removable dental prosthesis that joins the components on one side of the arch to those on the opposite side.
-
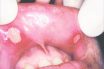
Major aphtha
A type of recurrent aphthous stomatitis that occurs in 10–15% of patients with the condition; usually manifested by the appearance of one or two large, painful ulcerations on movable, nonkeratinized oral mucosa, lasting for up to 6 weeks.
-
Maintenance
Procedures performed at selected time intervals to assist in the maintenance of the prosthetic reconstruction, periodontal and peri-implant tissue health. To keep in an existing state, that is, to continue to run or shut down. There are several types of maintenance programs: planned, preventive, corrective, predictive, etc. When dieting, caloric intake equals caloric expenditure. Term…
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Imaging that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce high‐quality two‐ or three dimensional images without use of ionizing radiation (X‐rays) or radioactive tracers. During an MRI scan, a large cylindrical magnet creates a magnetic field around the patient through which radio waves are sent. Medical MRI most frequently relies on the relaxation properties…
-
Magnetic attachment
Retentive device mainly used for retention of overdentures.