Category: M
-
Mattress suture
Suture made by a double penetration of the flap(s), not crossing over the incision line. Its purpose is to hold together the deeper tissues in order to reduce the tension of a flap upon approximation. It may be done in a horizontal or vertical direction. A suture made with a loop on each side of…
-
Matrix metalloproteinase(s) (MMPs)
A group of zinc‐and calcium‐dependent proteinases that degrade components of the extracellular matrix, such as collagen. These proteinases play a central role in many biological processes.
-
Matrix component
The part of an attachment designed specifically as a receptacle for the matching or mate component (patrix), such that when engaged it provides mechanical retention. Attachment systems that use mechanical retention are available in various designs.
-
Matrix
An intricate network of natural or synthetic fibers that aids in the reinforcement and development of tissues by supplying a scaffold on which cells may grow, migrate, and proliferate. The female part of an attachment. The noncellular material in which bone and cartilage cells are embedded. An amorphous mass of cells forming the basis of…
-
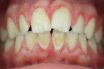
Materia alba
Loosely adherent, white curds of matter composed of dead cells, food debris, bacteria, and other components of the dental plaque that lack the organized structure of a biofilm and are found on tooth or oral implant prosthesis surfaces. A whitish food residue that adheres to the teeth near the gums. The thick white paste formed…
-
Masticatory system
The organs and structures functioning in mastication, including the jaws, teeth with their supporting structures, temporomandibular articulation, mandibular musculature, tongue, lips, cheeks, oral mucosa, and associated nervous system.
-
Masticatory mucosa
Keratinized and attached oral mucosa of the gingiva and hard palate. The gingiva and the mucosal covering of the hard palate. Those areas of the mucosa of the mouth that have become keratinized due to the friction and abrasion of the masticatory process, especially the gingivae and hard palate.
-
Mastication
Act of grinding or crushing food (chewing) preparatory to deglutition and digestion. The masticatory cycle involves three‐dimensional movements of the mandible observed in the frontal, horizontal, and sagittal planes. Chewing, grinding, and tearing foods with the teeth while it is mixed with saliva. The process of chewing food, which is dependent upon intact jawbones and…
-
Master impression
The negative likeness reproduction of the dental arch characterized by high dimensional accuracy and surface detail made for the construction of a master cast on which the prosthesis will be fabricated.
-
Master (definitive) cast
Final cast used for the fabrication of a prosthesis.