Category: M
-
Microleakage
Microscopic movement of fluids or contaminants across a barrier or between chambers that cannot be observed without magnification. The microscopic seepage of oral fluids between the interface of the tooth and a dental restoration. Microleakage may lead to sensitivity or discoloration of the tooth. Caused by discrepancies between the coefficient of thermal expansion of the…
-
Micro‐interlock
Fixation by mechanical interlocking of bone to micro‐irregularities at textured dental implant surfaces, including those created by grit blasting, coating, or ion bombardment, which have dimensions in the range of less than 10 microns.
-
Micrognathia
Abnormal smallness of the jaw, particularly the mandible, that can be congenital or acquired. A condition in which one jaw is unusually smaller than the other. Marked undergrowth of one jaw relative to the growth of the other. Abnormal smallness of jaws, especially the lower jaw. An unusually undersized lower jaw, referred to as micrognathia,…
-
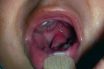
Microglossia
Having an abnormally small tongue. A condition in which a person has an unusually small tongue. A tongue that is smaller than usual. This condition is frequently linked to a genetic disorder and is commonly accompanied by micrognathia, which is a condition characterized by an abnormally small jaw.
-
Microgap
Microscopic space between two components, specifically between an implant and an abutment. It is usually considered to be a source of chronic irritation or contamination creating an inflammatory response.
-
Microcrack
In porcelain, one of the numerous surface flaws that contribute to stress concentrations and results in strengths below those theoretically possible.
-
Microbiota
The microscopic living organisms of a region. Microscopic organisms within a defined area, organism, or physiological environment. The entirety of microorganisms inhabiting the human body (or any other ecological habitat) as a collective entity.
-
Microbial resistance
The ability of microorganisms to resist the effects of antibiotics; usually due to chromosomal mutation or the transfer of resistant genes from already resistant organisms; mechanisms include antibiotic enzymatic destruction.
-
Microaerophilic
Refers to bacteria that grow under conditions of reduced oxygen concentration. Used to describe conditions in which the oxygen concentration is lower than atmospheric levels. Requiring a relatively low oxygen tension for growth. There may be a requirement for a higher carbon dioxide concentration. Describing microorganisms that grow best at very low oxygen concentrations (i.e.…
-
MIC (abbrev)
Minimum inhibitory concentration.