Category: I
-
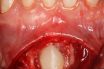
Impaction of tooth
Developmental disturbance in which a tooth does not fully erupt into occlusion. It may be a tooth bud or fully developed tooth surrounded by bone, either partially or fully. The most frequently impacted teeth are mandibular third molars.
-
Impacted tooth (impaction)
An unerupted or partially erupted tooth so positioned that complete eruption is unlikely. A tooth which is held against another tooth and so cannot grow normally. A tooth blocked from appearing in the mouth because the jaw is already overcrowded with teeth. An impacted tooth can become infected and painful, requiring extraction; it can also…
-
Immunosuppression
A reduced response of the immune system caused deliberately, by medications or radiation, or not deliberately, by malnutrition, cancer or certain diseases such as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Involves a process that reduces the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Suppression of the body’s immune system and its ability to fight infections and other…
-
Immunologic response
Bodily defense in reaction to an invading substance (antigen, such as virus, fungus, bacteria, or transplanted organ) that produces a response, including antibody production, cell‐mediated immunity, or immunologic tolerance.
-
Immunoglobulin
A glycoprotein composed of “heavy” and “light” peptide chains; functions as antibody in serum and secretions. There are five major classes (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, and IgD), each with specialized functions. A protein that acts as an antibody. A member of a family of proteins from which antibodies are derived. There are five main classes…
-
Immunofluorescent microscopy
A process in which cells or tissues are labeled with fluorescent dye‐conjugated antibodies and examined with an ultraviolet light microscope. Used to identify certain structures or markers on cells.
-
Immunodeficiency
A condition where elements of the immune system are defective or deficient and the individual may not be able to fight infections adequately; may be congenital (primary) or acquired (secondary). A state in which the immune system’s ability to fight infectious disease is compromised or entirely absent. The decreased ability of the body to fight…
-
Immunocompetence
Ability or capacity to develop a normal immune response following exposure to antigen. The ability to develop an immune response following exposure to an antigen. The ability of the body’s immune system to respond to pathogenic organisms and tissue damage. This ability may be diminished by drugs specifically developed to inhibit immune cell function (e.g.,…
-
Innate i
Congenital. Nonspecific immunity present from birth. Responsible for the initial protection from infectious agents previously unseen by the host. Composed of soluble immune proteins (including complement) and phagocytes.
-
Immunity
A state of host‐mediated resistance defending against foreign agents or organisms encountered on or within the tissues that is capable of distinguishing between self and nonself. Nonsusceptibility to the invasive or pathogenic effects of foreign microorganisms or to the toxic effect of antigenic substances. The ability to resist infection and to heal. The process may…