Category: G
-
Grandparent’s rights
The legally supported ability of grand¬ parents to visit their grandchildren even if the parents have separated or divorced. In practice, many parents wish to continue relationships between grandparent and grandchild, but some do not, and their attempt to bar such contact has led to a great deal of lobbying for legal protection of grandparents’…
-
Grade-equivalen
A score indicating how a student’s performance on a test ranks in terms of the average performance of students of various grades on the same or a similar test. For example, if the norm for students in the fifth month of seventh grade is a score of 85 on a particular test, and your sixth-grader…
-
Gifted child
A child who has very superior abilities, especially in academic areas, but also sometimes in artistic or athletic fields. It is widely agreed that such children have special needs and benefit most from adapted education programs. However, the definition of “gifted” varies widely. The classic early description focused on a gifted child’s special combination of…
-
Genu varum
An abnormality in which the legs bend outward at the knees; medical parlance for “bowlegs.” Congenital deformity in which the lower legs are bent away from the midline; also known as bowleg.
-
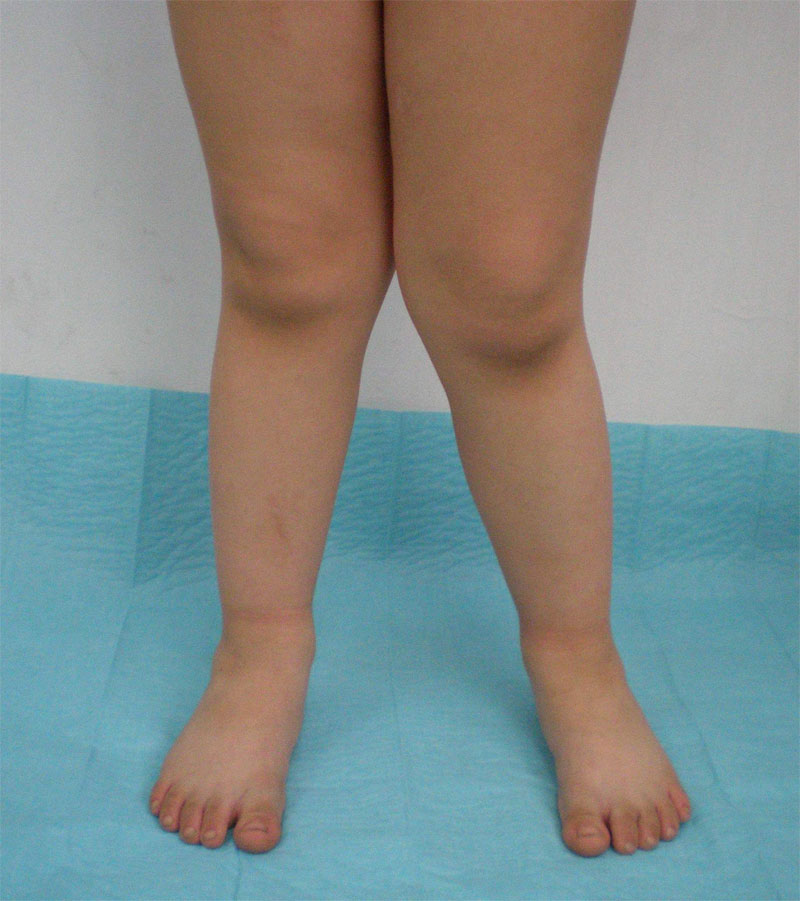
Genu valgum
An abnormality in which the legs bend inward, with the knees close together; medical parlance for “knock- knees.” Congenital deformity in which the lower legs are bent medially; also known as knock-knee. Abnormal incurving of the legs, resulting in excessive separation of the feet when the knees are in contact. The medical term for knock-knee…
-
Genetic inheritance
The pattern by which information is passed from parents to child, creating a unique individual. The basic units of inheritance are genes, molecules of DNA in a cell’s nucleus that are organized in linear sequence on 23 threadlike pairs of structures called chromosomes. One pair, the sex chromosomes, determines the new being’s gender. A normal…
-
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures are one of the most common childhood neurological disorders. The seizure involves synchronous bilateral electrical epileptical discharges; therefore, the first signs reflect involvement of both hemispheres of the brain. The seizure, however, can begin in a focal area of the brain (or one hemisphere) as a partial seizure and spread to other…
-
Giant axonal neuropathy
Giant axonal neuropathy (GAN) is a rare neurologic disorder characterized by slowly progressive peripheral neuropathy and signs of central impairment. Common symptoms include muscle weakness and wasting, visual impairments, ataxia, and, at later stages, mental decline and dementia.
-
Genetic microcephaly
Microcephaly is an anomaly of the central nervous system where head circumference is significantly (3 standard deviations) smaller than average given the age and gender of the infant or child (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke [NINDS], 2000). This reduced head size usually occurs as a result of diminished brain mass (micrencephaly) but can…
-
Growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency is a condition resulting in impaired physical growth, caused by a partial or total absence of the growth hormone produced by the pituitary gland. The affected child will have normal body proportions and yet often look younger than his or her peers (Human Growth Foundation, 2000). If other pituitary hormones are lacking,…