Category: F
-
Fulguration
Tissue destruction with high-frequency electrical sparks. In medicine, the burning away of a growth by means of a cautery. The removal of a growth such as a wart by burning with an electric needle. Destruction of unwanted tissue by the use of electrical current in the form of sparks. The destruction with a diathermy instrument…
-
Fowler’s position
A semi-sitting position, usually at 45 degrees, used to facilitate breathing and drainage. Semireclining in bed, with head of bed elevated. A semi-sitting position. The head of an adjustable bed can be elevated to the desired height to produce angulation of the body, usually 45° to 60°. The knees may or may not be bent.…
-
Fluorescein angiography
A procedure in which light-sensitive material is injected into a blood vessel. Diagnostic procedure in which fluorescein, an orange fluorescent dye, is injected intravenously, traveling to the retinal artery in the eye and causing it to glow fluorescent green on flash photography of the retina. A test using a special camera to photograph blood vessels…
-
Fasciculation
Involuntary contraction or twitching of muscles. Small muscle movements which appear as trembling skin. Uncontrollable, localized contraction of a single muscle group that is visible through the skin. The twitching of an isolated muscle, which may or may not be related to a neuromuscular disorder. Brief spontaneous contraction of a few muscle fibers, which is…
-
Fibrillation (ventricular)
Cardiac arrhythmia characterized by the rapid, incomplete, and uncoordinated contractions of the muscle fibers of ventricles of the heart. Can lead to cardiac arrest. An arrhythmia in which the walls of the ventricle of the heart quiver rather than beat regularly. This causes an interruption of the flow of blood and lack of oxygen to…
-
Fecalith
Hard, solid, intestinal mass formed around a core of fecal material. Hard mass of feces in the colon, evacuated manually or by means of an oil enema. Hardened feces that become a stone-like mass, occurring most often in the appendix or a diverticulum. A hard, stone like mass of feces. A fecalith can be responsible…
-
Fetus
Human conceptus growing in the uterus usually called a fetus from the seventh or eighth week of pregnancy. The developing young in the uterus after the second month pregnancy. The fertilized egg from the end of the embryonic period through birth. An unborn baby from two months after conception until birth, before which it is…
-
Fructooligosaccharide
Natural fiber that exists in unprocessed fruits and vegetables.
-
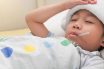
Fever
Elevation of body temperature above normal 36.8º (98.4º F). A high body temperature, above the normal 98.6°F (37°C). Most infectious illnesses cause fever, which is a sign that the body’s temperature-regulating mechanism has been affected by the infection. An elevation of body temperature above normal. Normal human body temperature is designated as 98.6° F or…
-

Fullers teasel (Dipsacus sativus)
Comb-like flowerheads were once an important article of commerce for raising nap on woollen cloth. Excellent in dried arrangements. Leaf basins collect water which is valued as an eyewash.