Category: E
-
Einthoven
Dutch physiologist who devised the first electrocardiograph; he was the first to link this recording of the heart’s electrical activity with its mechanical contraction. The original electrocardiogram (EKG, ECG) had three leads, or points of reference, which could be drawn as a triangle (Einthoven’s Triangle).
-
Effervescent
Giving off bubbles; charged naturally or artificially with carbon dioxide or other gas. Bubbling; rising in little bubbles of gas.
-
Earache
Pain in the ear; it may be caused by ear disease or by infection or disease of the nose, mouth region, throat, and other nearby areas; also called otalgia. Pain in one or both ears, medically termed otalgia, which may be sharp and stabbing or dull and throbbing. When earaches are severe and persistent, an…
-
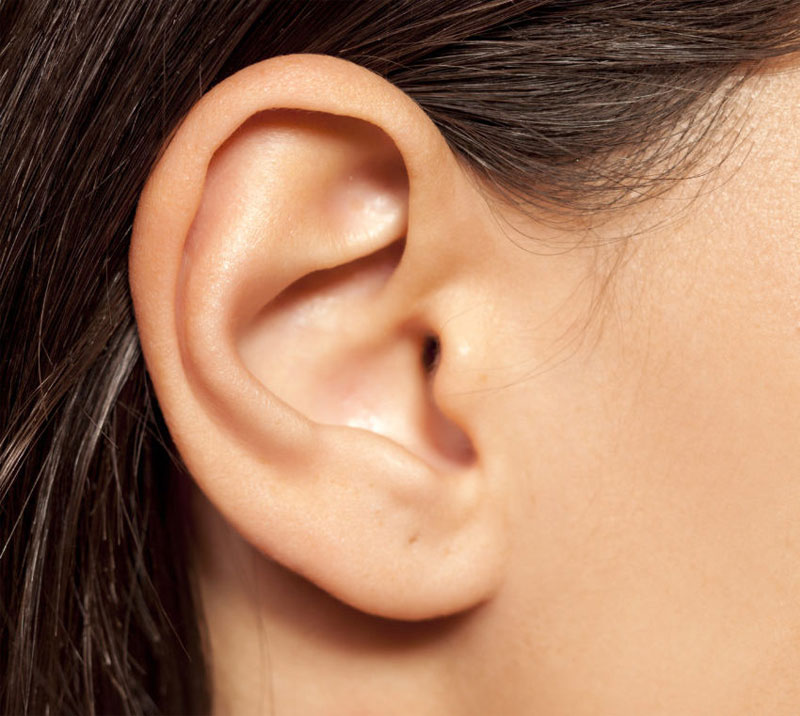
Ear
Hearing and balance organ, including three general structures; the outer (external) ear; the middle ear, including the eardrum cavity and the three tiny bones that transmit the hearing vibrations; and the inner (internal) ear, including the main organ of hearing (the organ of Corti) and the balance mechanism. The organ for hearing and balance. The…
-
Eugonic
Literally ‘easily seeded’, bacteriologically the term implies easy cultivation and is especially used in connection with the mycobacteria. Growing rapidly in culture; said of some bacteria.
-
Ethylene oxide sterilization
Gaseous disinfectant for the treatment of heat-labile materials such as plastics and rubber, 10 per cent of the oxide (in a diluent such as CO2), being introduced at pressure between pre – and post-vacuum phases.
-
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Causative organism of swine erysipelas. Small and possibly micro- aerophilic Gram-positive bacillus which on occasion shows true branching. Transmissible to man (erysipeloid) and many animals, fish and birds. A species of gram-positive, filamentous bacilli that causes erysipeloid.
-
Erysipelothrix muriseptica
Causative organism of epidemic mouse septicaemia, possibly identical with Ery. rhusiopathiae.
-
Enterobacter liquefaciens
Psychrophilic species—biochemical reactions affected by incubation temperature. Inositol fermented, adonitol not; gelatin liquefied (more rapidly than is the case with E. cloacae’).
-
Enterobacter cloacae
Type species of the Enterobacter group, and formerly known as Aerobacter cloacae or Cloaca cloacae. Liquefies gelatin; does not ferment inositol. A species that, along with E. agglomerans, accounts for most nosocomial infections caused by this genus, especially those due to intravenous line contamination.