Category: E
-
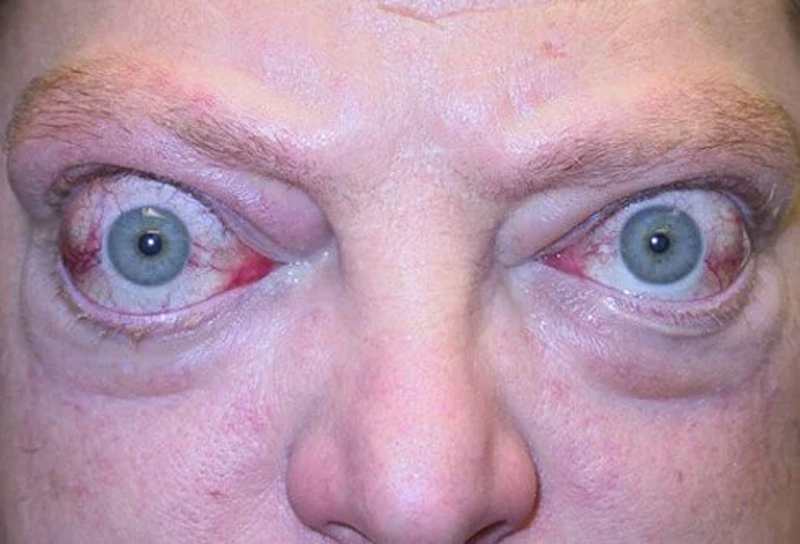
Eye graves disease
Swelling and bulging of the eyes caused by excessive production of thyroid hormones; also known as Graves ophthalmopathy. The thyroid gland, located to the front and sides of the windpipe (trachea) just above the breastbone (sternum), produces thyroid hormones that control important body processes, such as the rate of metabolism, body temperature and muscle tone…
-
Eyelid surgery
A procedure that tightens bagging or drooping eyelids by removing excess tissue; also called blepharoplasty. Typically, eyelid surgery is performed for cosmetic reasons; baggy eyelids make an individual look older and more tired than he or she feels. Cosmetic eyelid surgery can be performed alone or along with another cosmetic surgery, such as a facelift.…
-
Examination of eye
A series of tests performed to measure the eyes’ ability to see clearly and to screen for common eye diseases. If one sees normally, an eye examination every 3 to 5 years during adulthood until age 50 years is recommended. After that, the eyes should be examined more frequently. If one wears or needs glasses,…
-
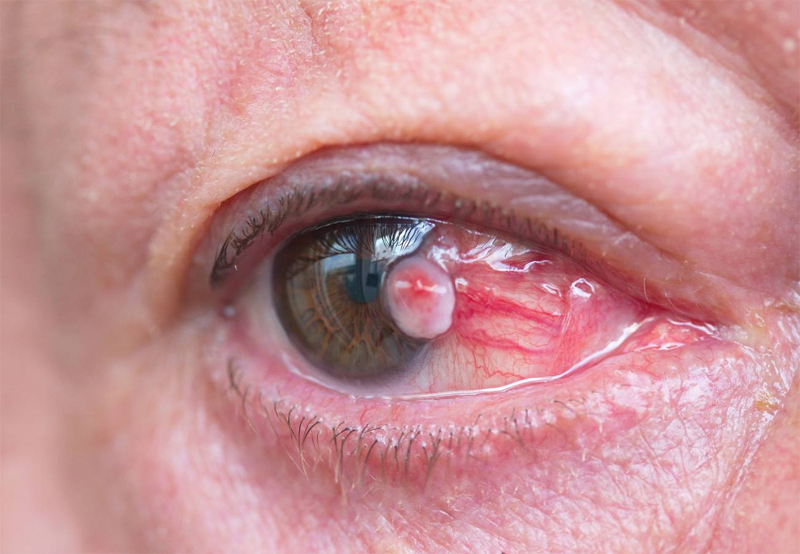
Eye tumors
Abnormal growth of tissue in the eyeball or its surrounding structures. Eye tumors can be benign, or noncancerous: that is, their growth is confined to a particular body structure and they do not metastasize or spread throughout the body. Some are malignant (cancerous): that is, they can spread and threaten life.
-
Eye injury
Physical damage to the eye or its surrounding tissue as a result of accident or mishap. Eye injuries may be caused by foreign objects (most commonly, contact lenses), blunt trauma, burns, or penetrating injuries, the most traumatic and dangerous type of damage.
-
Explosive disorder
A mental illness characterized by repeated episodes of serious violence against people or property that occur with little or no provocation. Relief follows the violent episode, and the individual usually expresses upset, remorse, regret, or embarrassment. Since explosive disorder is very rare, little is known about what causes of the disorder. Similar outbursts can be…
-
Strengthening exercise
Physical activity that builds strength in the muscles. Strengthening exercises may also improve posture and balance. Exercises that strengthen muscles help support the joints, which can help reduce the symptoms of arthritis. Improved strength may help decrease the risk of injuries and improve a person’s ability to perform many activities of daily life.
-
Evoked responses
Tests that assess the ability of information to travel to the brain. There are three commonly used evoked response tests: visual evoked response (VER), which assesses how well information travels from the eyes to the occipital lobes (visual cortex); brain stem auditory evoked response (BAER), which assesses neurological function and diagnoses nervous system abnormalities and…
-
Esophagogram
A series of X rays of the esophagus. An esophagogram is also known as a barium swallow or an upper GI series.
-
Esophagectomy
Partial or total removal of the esophagus (the tube that connects the throat and stomach). An esophagectomy is usually performed to treat esophageal cancer. In some cases, an esophagectomy is performed to control severe recurrent bleeding caused by esophageal varices. Surgical removal of all or a portion of the esophagus. A surgical procedure to create…