Category: D
-
Dental crown
The visible part of the tooth that normally protrudes above the gum line. A dental crown is also the name for the artificial replacement placed over a dental implant or the remaining structure of a natural tooth, most often because of a fracture or tooth decay. Dental crowns are sometimes called caps; they restore the…
-
Dental cavity
A hole in a tooth caused by decay. A cavity is caused by the formation of dental plaque (see plaque, dental), which is made up of bacteria, food particles, and saliva. The bacteria interact with sugars in food particles that remain in the mouth and on the teeth to form acid, which dissolves the calcium…
-
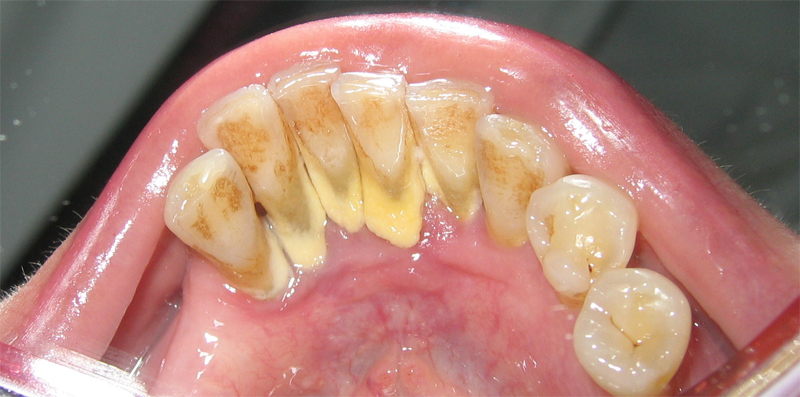
Dental calculus
A mineralized, porous deposit that hardens and adheres to the crowns and roots of the teeth. Dental calculus, also called tartar, is caused by the accumulation of plaque. Once calculus has formed, it traps more plaque. The bacteria in the plaque produce toxins that irritate the gums and can cause the destruction of fibers that…
-
Dental bridge
A dental appliance of false teeth that is attached to natural teeth on either side. A fixed bridge is attached to the teeth that have been filed down in order to be fitted with crowns. Fixed dental bridges are more commonly used than removable, partial denture bridges, except in cases in which there are several…
-
Dental braces
Mental or plastic appliances worn on the teeth that apply steady, gently pressure over an extended period to move teeth into the proper position.
-
Dental Bleaching
A cosmetic process to whiten teeth that have become discolored. Dental bleaching is considered safe for the teeth and gums when supervised by a dentist, who can determine whether a person’s teeth can be lightened and what type of bleaching system is appropriate. The most immediate results involve applying a bleach solution to the teeth,…
-
Disease of bartholin glands
Disorders affecting the two Bartholin glands, located on either side of the vaginal entrance, that secrete lubricating fluid during sexual arousal. The gland openings can become blocked from infection or injury. As a result, a Bartholin cyst may form, usually causing no symptoms. However, if the cyst (a fluid-filled sac) becomes infected and an abscess…
-
Drug therapeutic monitoring
Tests performed on blood to determine therapeutic levels or identify toxic amounts in blood of drugs such as antibiotics.
-
Doppler ultrasonic flowmeter
Device that measures blood flow in blood vessels to diagnose the extent of various circulatory diseases and disorders.
-
Dead on arrival
A term used for persons found to be dead at home, in a public place, or who died before reaching the hospital.