Category: D
-
DNA forensic testing
The use of DNA fingerprinting to identify suspects in criminal proceedings. Just as they collect fingerprints, criminal investigators routinely take biological tissue samples, such as bloodstains, semen, or saliva, from crime scenes. DNA evidence collected from a crime scene can link a suspect to evidence or eliminate a suspect.
-
DNA fingerprinting
A laboratory procedure in which individuals are identified by their deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA fingerprinting is based on the fact that everyone has a unique set of genes and DNA. The technique, also called DNA typing or DNA profiling, is used by forensic scientists and police laboratories as evidence in criminal proceedings or t o…
-
Diskography
An imaging technique used to locate the source of back pain caused by an injured disk. In diskography, a solution is injected into the specific disks believed to be causing pain, as well as into neighboring disks. A special X ray called a diskogram is taken, which is often used before back surgery to identify…
-
Disclosing agents
Stains in tablet or liquid form that adhere to the plaque on teeth. Plaque contains bacteria, mucus, and food particles that build up if the teeth are not brushed and flossed regularly. Dental plaque cannot be observed unless it is stained. When chewed, these tablets stain the plaque red so those areas of the teeth…
-
Didanosine
An antiviral drug used in the treatment of HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) and AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Didanosine (Videx) stops the growth of the HIV. Didanosine is also called ddl. It is not a cure for AIDS, although in combination with other drugs, it can slow the disease process and prolong a person’s life. The…
-
Dextromethorphan hydrobromide
A cough suppressant. Dextromethorphan is a nonprescription drug that suppresses a dry, unproductive cough without the addictive, sedative, and pain-relieving effects of codeine. It is available under many brand names as lozenges, syrups, and chewable tablets.
-
Desmoid tumor
An abnormal growth that is firm, fibrous, and rubbery. Desmoids most often occur in the abdominal wall, but may also develop in the head, neck, arm, or legs. In the abdomen, these tumors are most common in women who have had children. Growths may also develop at the site of old surgical incisions. Most desmoid…
-
Dermatographism
Hives produced by rubbing, stroking, or friction on the skin; also known as dermographism. In dermatographism, histamine is released, causing capillaries (small blood vessels) to dilate, leading to redness and localized swelling. Dermatographism is a nonallergic cause of hives and is usually brought on by scratching. Long, raised, narrow, and itchy hives exactly follow the…
-
Dermatofibroma
A nodule (a solid mass of tissue) or small, round bump on the skin. Dermatofibromas may be pink or brown and are commonly found on the arms and legs of adults. They are believed to follow mild trauma or injury. Dermatofibromas are common, common, benign (not cancerous), and painless. However, they may persist indefinitely. A…
-
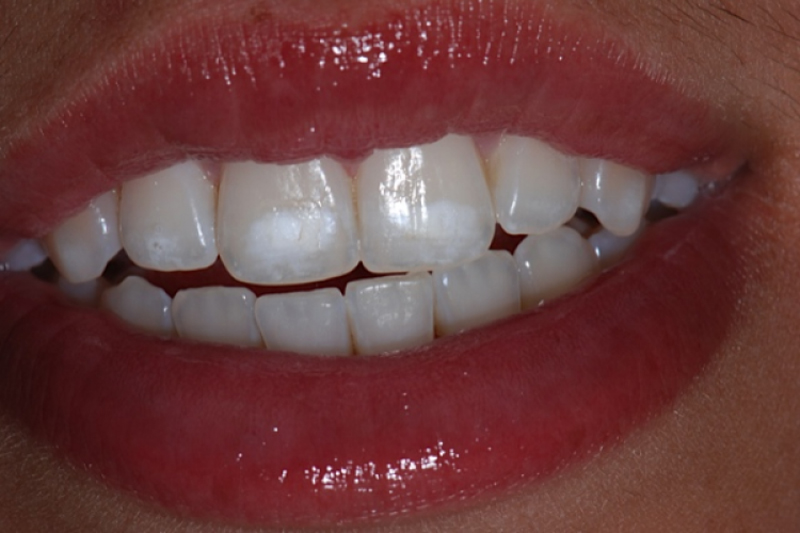
Dental decalcification
The loss of calcium from the hard enamel covering the teeth. The enamel is made up almost entirely of calcified material. The result of dental decalcification is the loss of the hard, smooth tooth surface, which becomes chalky and porous as the enamel dissolves. This makes the tooth more susceptible to decay. The condition is…