Category: B
-
Bacteriophage typing
Determination of the subdivision of a bacterial species by a type-specific bacteriophage.
-
Buschke-Loewenstein tumor
A giant condyloma acuminata, typically found on the genitals or anus, caused by infection with papilloma virus. In men, it is almost always found under the foreskin (it is rarely reported in circumcised men). It may transform into a verrucous carcinoma and cause deep local tissue invasion.
-
Brown tumor
A benign fibrotic mass found within the bone of patients with unchecked hyperparathyroidism. The tumor appears brown on gross examination because it contains blood and byproducts of the metabolism of hemoglobin, such as hemosiderin.
-
Biological transmission
A condition in which the organism that transmits the causative agent of a disease plays an essential role in the life history of a parasite or germ.
-
Blastocyst transfer
An assisted reproduction technique in which a zygote created by in vitro fertilization is incubated in the laboratory to the pre-embryonic stage of the blastocyst before being placed in the uterus.
-
Bowel training
A program for assisting adult patients to reestablish regular bowel habits. Patients with chronic constipation, colostomies, fecal incontinence, or spinal cord injuries affecting the muscles involved in defecation may benefit from bowel training. Assessments include determining the etiology and duration of the bowel problem, the normal pattern, the use of enemas, suppositories, or laxatives to…
-
Brawny trachoma
Trachoma with general lymphoid infiltration without granulation of the conjunctiva.
-
Botulinus toxin
A neurotoxin that blocks acetylcholine release, produced by Clostridium botulinum, the causative organism for botulism. Seven types of the toxin have been identified.
-
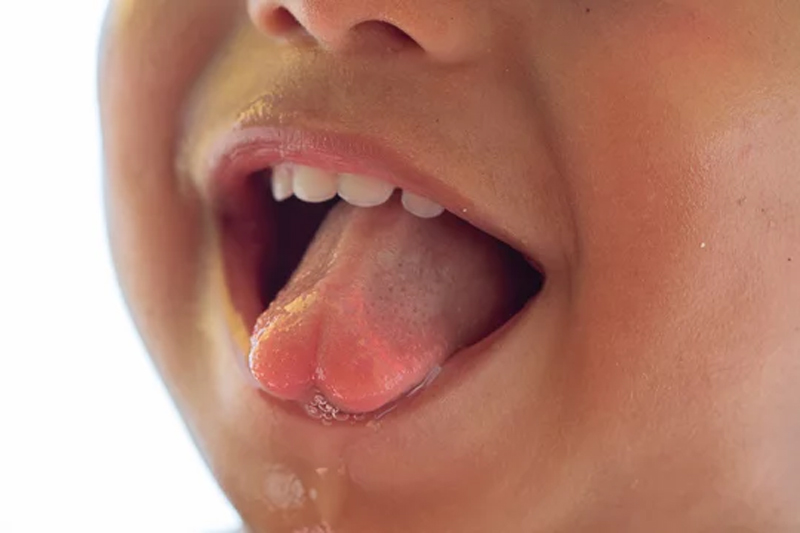
Bifid tongue
A tongue with a cleft at its anterior end.
-
Bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue
Lymph nodules that contain clusters of T and B lymphocytes and macrophages within the mucosa of the bronchial wall; a component of the mucosal immune system that defends all mucosal surfaces against pathogens.