Category: B
-
Basal body temperature
Body temperature taken immediately after awakening in the morning and before getting out of bed. Typically, the BBT is used by women to identify the days during the menstrual cycle when ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovary) takes place. A woman’s temperature often falls by a few tenths of a degree during…
-
Balloon angioplasty
A minimally invasive procedure to open arteries narrowed or blocked by fatty deposits, a disease known as atherosclerosis. The technical name for balloon angioplasty when done on the coronary arteries is percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA), which means that the procedure is performed through the skin (percutaneous) and inside an artery (transluminal) that feeds the…
-
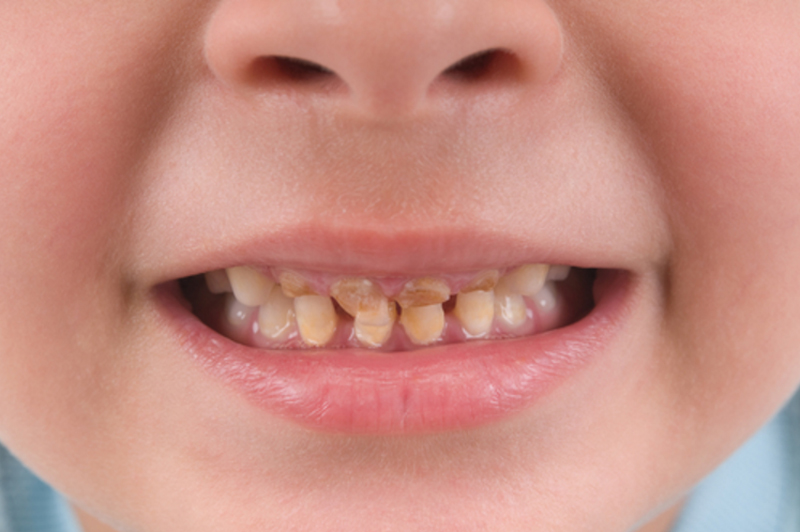
Baby bottle tooth decay
Tooth decay in children younger than 3 years caused by sugar-containing liquids. The main cause of bottle dental decay is the practice of allowing a child to suck on a bottle of milk, formula, fruit juice, or other sweet drinks throughout the day or while in bed. These liquids cling to the teeth for hours,…
-
Brucella agglutinins
Antibodies elevated in blood of patients with brucellosis.
-
Breast stimulation stress test
A test in which a pregnant woman’s breasts are stimulated to contract the womb. During contractions, fetal well-being is assessed by recording and evaluating the fetal heart rate.
-
Bone X-ray
An X-ray study of bone to determine whether fracture or disease is present.
-
Body surface area
A calculation based on a person’s height and weight, used to determine the appropriate amount of food, fluid, and medication as needed in various circumstances. The surface area of the body expressed in square meters. Body surface area is an important measure in calculating pediatric dosages and drug dosages in chemotherapy, managing burn patients, and…
-
Bleeding and clotting time
Two blood tests, generally performed at the same time, to show how rapidly the small blood vessels constrict to stop bleeding, and how effectively the blood’s clotting mechanisms are working.
-
Biplane cerebral angiography
An X-ray study of the blood vessels in the brain after injection of contrast medium, showing the structures from the side (laterally) and front-to-back (anteroposteriorly).
-
Biliary drainage test
A test of bile fluid drawn from the duodenum (the portion of small intestine adjacent to the stomach) to check for white blood cells, cholesterol, crystals, or parasites.