Category: B
-
Bone cyst
An abnormal closed cavity or sac lined with tissue and filled with fluid that originates in the bone tissue and is usually noncancerous (benign). Bone cysts are rare, tend to occur in children between the ages of 5 and 15 years, and generally develop in long bones, such as the upper arm bone (humerus) or…
-
Bone abscess
A pus-filled pocket or cavity located on or in the bone and surrounded by inflamed tissue. The bacterial infection that most commonly gives rise to a bone abscess is caused by a staphylococcal infection. Bone abscesses are rare and potentially fatal. They are treated with a surgical procedure to drain the abscess, as well as…
-
Body piercing
The practice of creating holes in body parts for cosmetic purposes. Body piercing enables people to wear jewelry in such body parts as the earlobes, lips, nose, navel, eyebrows, nipples, and genitals. Body piercing has been practiced in almost every society, chiefly involving ears, nose, and mouth. Nontraditional body piercing has become increasingly popular in…
-
Blow-out fracture
A break in the floor of the bony socket (orbit) surrounding the eye. The usual cause is a hard blow from a nonpenetrating blunt object. The fracture may entrap some of the muscles that move the eye, causing double vision, especially when the person looks up. Other symptoms include bruising around the eye, protrusion of…
-
Blood smear
A laboratory test that provides information about the number, type, and shape of blood cells; also known as a peripheral smear or differential stain. Once a blood sample has been drawn, the number of white and red blood cells relative to other types of blood cells is counted, any abnormalities in cell shape are noted,…
-
Blood pressure cuff
The inflatable band placed around the upper arm to measure blood pressure. The blood pressure cuff is part of an instrument called a sphygmomanometer, the most accurate method of measuring blood pressure.
-
Blood donation
The collection of whole blood or its components from a person. Whole blood donation takes about 10 minutes, while apheresis (in which components of a donor’s blood are collected) requires approximately 1½ hours. Blood collection is strictly regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Donated blood is used for persons undergoing bone marrow transplant,…
-
Bladder cancer
Abnormal growth and cell division of the tissues of the bladder, the hollow organ that holds urine. Most bladder cancers are transitional cell carcinomas, which are cancers that begin within the layers of the cells lining the inner wall of the bladder. When bladder cancer is confined to the surface layer, it is called superficial…
-
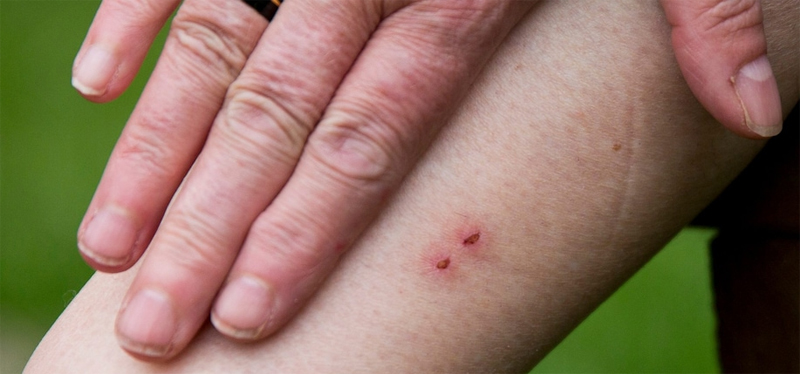
Reptile bites
Most reptiles, such as turtles and snakes, are not poisonous, and their bites can be treated with first aid, including thorough washing of the area, applying antibiotic cream or ointment, and bandaging. The best way to reduce the risk of being bitten by a reptile is not to handle them. Only people with proper training…
-
Bites and stings
Wounds delivered to people through contact with humans, animals, and insects. Bites and stings can be minor or serious. Medical treatment should be sought if the person bitten develops swelling, redness, or pus or has not had a tetanus shot in 10 years, or if the wound requires stitches. Potentially dangerous bites and stings can…