 Is an abscess larger than a boil, usually with one or more openings draining pus onto the skin.
Is an abscess larger than a boil, usually with one or more openings draining pus onto the skin.
An extensive dangerous form of boil having a flat surface that discharges pus from multiple points and occupies several inches of skin surface.
A localised staphylococcal infection, which goes deep into the tissue.
Swollen lumps or masses under the skin due to skin infections that often involve a group of hair follicles.
A many-headed boil.
Cluster of boils or abscesses (resulting from infection with Staphylococcus bacteria) deep under the skin from which pus escapes to the skin surface. Treatment is by surgical drainage, antibiotics, and compresses.
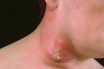
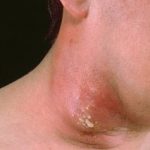
A cluster of painful, pus-filled boils on the skin. A boil results when a hair follicle becomes infected with staphylococcal (staph) bacteria. In a carbuncle, boils in adjacent follicles expand and join to form a mass with multiple drainage points. Although they can develop anywhere, carbuncles are most common on the back and the buttocks. They are usually the size of a pea but may grow as large as a golf ball.
A collection of boils with multiple drainage channels. The infection is usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus and normally results in an extensive slough of skin. Treatment is with antibiotics and sometimes also by surgery.
A painful, deep abscess of the skin involving multiple hair follicles, formed by the merger of two or more boils (furuncles) and draining through multiple follicular openings.
Inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue caused by staphylococci; similar to a furuncle but larger.
A substantial and profound skin abscess characterized by the presence of a cluster or group of boils.
Carbuncles are clusters of interconnected boils characterized by painful, inflamed hair roots filled with pus. Typically, these skin lesions are caused by an infection with the bacterium Staphylococcus Aureus. The most commonly affected areas are the back of the neck and the buttocks. Carbuncles primarily occur in individuals with compromised immune systems, particularly those with diabetes mellitus.
The typical approach to treating carbuncles involves the use of antibiotic medication. Additionally, the application of hot compresses can help facilitate the bursting of pus-filled heads, providing relief from pain. In some cases, if a carbuncle persists and spontaneous drainage and healing do not occur, incision and drainage may be necessary. This procedure involves the removal of the carbuncle’s core to promote drainage and facilitate the healing process.
An infection that extends through the entire depth of the skin, triggered by the pus-producing bacterium known as staphylococcus. It gives rise to a substantial infected area from which pus is discharged through multiple openings in the skin, resulting in a sieve-like appearance. A carbuncle is profoundly incapacitating, exceedingly painful, and significantly more severe than a boil, which is an infection of a hair follicle caused by the same microorganism.