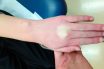
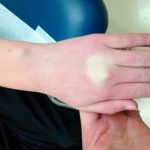
 To make or become white or pale, usually in reference to periimplant or periodontal soft tissues (e.g., during prosthetic try‐in/insertion).
To make or become white or pale, usually in reference to periimplant or periodontal soft tissues (e.g., during prosthetic try‐in/insertion).
A unit operation in food processing in which raw food materials are immersed in hot water or exposed to live steam, hot gases or microwave energy.
Heat treatment given mostly to fruits and vegetables to inactivate enzymes, for example by short exposure to boiling water, steam or dry heat; or alternate hot and cold treatment given mostly to vegetables such as tomatoes for removal of the skin.
A processing technique involving brief exposure of foods to boiling water. Blanching wilts the leaf structure of plants, inhibits the peroxidation of fats and oils, and results in inactivation of a variety of enzymes that contribute to food spoilage.
Boiling water can be used to treat food in various ways, such as whitening it, preserving its natural color, loosening its skin, removing a strong or unpleasant flavor (e.g. too acidic or rank), or killing unwanted enzymes (in the case of vegetables that will be canned or frozen).