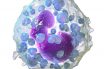
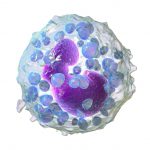
 A granular leukocyte containing substances that contribute to inflammation, including leukotrienes and vascular amines such as histamine and serotonin; important in hypersensitivity reactions.
A granular leukocyte containing substances that contribute to inflammation, including leukotrienes and vascular amines such as histamine and serotonin; important in hypersensitivity reactions.
A type of white blood cell with coarse granules within the cytoplasm and a bilobate (two-lobed) nucleus.
A type of white blood cell which has granules in its cytoplasm and contains histamine and heparin.
Granular leukocytes characterized by a relatively pale-staining, lobate nucleus and cytoplasm containing coarse dark-staining granules of variable size and stainable by basic dyes.
Type of white blood cell (leukocyte), with coarse granules that stain blue when exposed to a basic dye. Basophils normally constitute 1% or less of the total white blood cell count but may increase or decrease in certain diseases.
One type of white blood cell comprising less than 1 percent of all leukocytes.
A cell or part of a cell that stains readily with basic dyes such as methylene blue.
In the realm of cellular components found within the bloodstream, there exists a particular type of white blood cell characterized by its segmented structure. These cells possess large granules with a distinct dark blue-black hue and play a significant role in allergic reactions by releasing a chemical substance known as histamine.
Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell that contribute to both inflammatory and allergic reactions within the body.
A medical term used to describe cells or tissues that readily absorb basic dyes.