Author: Glossary
-
Tendon
Strong fibrous connective tissue that connects the fascia of a muscle to bones or muscles to muscles. Band of dense fibrous tissue forming the termination of a muscle and attaching muscle to bone with a minimum of elasticity. A tendon is a tough, fibrous cord of tissue that connects muscle to bone. The strong, inelastic…
-
Tempo transition
One of the three categories of transitions for deep-water exercise, this involves using a halftempo movement to create a smooth change from one move to another.
-
Tempo
The rate of speed at which the beats occur.
-
Talk test
A method used for measuring exercise intensity; one’s ability to talk during a workout can determine how hard the individual is working. A person is working above his or her maximum threshold if unable to speak while exercising. Talk test is used to adjust exercise intensity. You should be able to talk with a friend…
-
Tactile learner
A person who learns primarily through the sense of touch.
-
Tactile cue
A cue that is received by touch, such as a hand placed on the target muscle group or moving the limb only to the point of contact with an object.
-
Systole (systolic pressure)
The blood pressure when the heart is contracting; specifically, the maximum arterial pressure during contraction of the left ventricle. The time at which ventricular contraction occurs is called systole.
-
Synovial joint
A fully movable joint in which a synovial cavity is present between the two articulating bones. A joint where the two bones are separated by a space filled with synovial fluid which nourishes and lubricates the surfaces of the bones. Freely movable joint; types of synovial joints are ball-and-socket joint, gliding joint, hinge joint, and…
-
Synergist
Muscles that aid or assist in the action of the agonists but are not primarily responsible for the action; also referred to as guiding muscles. Muscle that combines with another and aids in its action. A drug that, when combined with another drug, produces effects greater than those when the drugs are taken separately, additive…
-
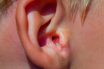
Swimmer’s ear
Caused by a bacterial infection resulting from failure to dry the ear adequately following swimming. Symptoms of this condition include itching, a greenish-colored discharge, pain when chewing, and a blocked feeling of the ear. A nonemergency condition that results from inflammation in the external ear canal created by the growth of infecting organisms, usually contracted…