Author: Glossary
-
Disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) gene
A gene that controls the birth of new neurons in addition to integration of those neurons into existing brain circuitry. This finding suggests that loss of the gene, as occurs in some cases of schizophrenia as well as bipolar disorders and major depressive disorder, may lead to an increased risk of compromised cognition and behavioral…
-
Displacement
A defense mechanism, operating unconsciously, in which emotions, ideas, or wishes are transferred from their original object to a more acceptable substitute; often used to allay anxiety. This mechanism is commonly observed in dreams and in the formation of phobias. In psychology, the transfer of hostility from the person or object causing the frustration to…
-
Disorientation
Loss of awareness of the position of the self in relation to space, time, or other persons; confusion. Mental confusion with respect to time, place, or person, disoriented. A condition in which someone is confused and does not know where he or she is. Mental confusion, characterized by a loss of awareness of space, time,…
-
Disorder of written expression
A learning disorder characterized by a substantially lower than expected level of writing skills given the subject’s chronological age, measured intelligence, and age appropriate education. An inability to draft grammatically correct phrases, sentences, or paragraphs, a disability that may impair advancement in school or work.
-
Disinhibition
In psychological terms, refers to freedom to act according to one’s inner drives or feelings, with less regard for restraints imposed by cultural norms or one’s superego. In neurology, refers to removal of an inhibitory, constraining, or limiting influence, as in the failure of cortical control over emotions or behaviors regulated by more primitive brain…
-
Disconnection syndrome
A term coined by the neurologist Norman Geschwind (1926–1984) to describe the interruption of information transferred from one brain region to another. Disturbance of the visual and language functions of the central nervous system due to interruption of the connections between two cerebral hemispheres in the corpus callosum, occlusion of the anterior cerebral artery, or…
-
Disability (psychiatric)
Lack of intellectual or emotional capacity or fitness. As defined by the federal government, “Inability to engage in any substantial gainful activity by reason of any medically determinable physical or mental impairment which can be expected to last or has lasted for a continuous period of not less than 12 full months.” Any physical or…
-
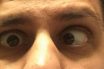
Diplopia
Double vision due to paralysis of the ocular muscles; seen in inhalant intoxication and other conditions affecting the oculomotor nerve. The perception of two images from a single object. A condition in which someone sees single objects as double. The condition in which a single object is perceived as two objects; double vision. Diplopia, also…
-
Diphenylbutylpiperidines
A subgroup of conventional antipsychotic drugs that includes pimozide (ORAP).
-
Diphenhydramine
An antihistamine medication used in general medical practice to treat cold or allergy symptoms and pruritus (itching) and used in psychiatry as an anxiolytic or to treat sleep distur bance. Marketed under the brand name benadryl. Antihistamine drug used to treat hay fever and other allergic reactions involving the nasal passages and also, sometimes, to…