Author: Glossary
-
Anthropometry
Body measurements used as an index of physiological development and nutritional status; a non-invasive way of assessing body composition. Weight for age provides information about the overall nutritional status of children; weight for height is used to detect acute malnutrition (wasting); height for age to detect chronic malnutrition (stunting). Mid-upper arm circumference provides an index…
-
Antacids
Bases that neutralise acids, used generally to counteract excessive gastric acidity and to treat indigestion: sodium bicarbonate, aluminium hydroxide, magnesium carbonate, and magnesium hydroxide. Drugs that neutralize or block the production of stomach acids. They are used to relieve heartburn, ulcers, and other digestive disorders. A substance used to neutralize hydrochloric acid produced by the…
-
Anovulation
Failure to ovulate spontaneously. A condition in which a women does not ovulate and is therefore infertile. Absence of egg production or release from the ovary. It may be caused by ovarian immaturity or postmaturity, pregnancy or lactation, dysfunction of the ovary, hormonal imbalance, or oral contraceptive pills; or be a side effect of other…
-

Anorexia nervosa
A psychological disturbance resulting in a refusal to eat, possibly with restriction to a very limited range of foods, and often accompanied by a rigid programme of vigorous physical exercise, to the point of exhaustion. The result is a very considerable loss of weight, with tissue atrophy and a fall in basal metabolic rate. It…
-
Anorectic drugs (anorexigenic drugs)
Drugs that depress the appetite, used as an aid to weight reduction. Apart from sibutramine (Reductil), most have been withdrawn from use; diethylpropion and mazindol are available but not recommended.
-
Anomers
Isomers of a sugar differing only in configuration at the hemiacetal carbon atom. Compounds with identical structures except for the arrangement of atoms around the anomeric carbon. An anomeric carbon has four different atoms or structural groups attached to it.
-
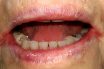
Angular stomatitis
A characteristic cracking and fissuring of the skin at the angles of the mouth, a symptom of vitamin B2 deficiency, but also seen in other conditions. Condition of the lips, mouth and cheeks characterised by cracks and fissures and caused by a bacterial infection.
-
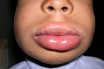
Angio-oedema
Presence of fluid in subcutaneous tissues or submucosa, particularly of the face, eyes, lips and sometimes tongue and throat; may occur during an anaphylactic reaction.
-
Aneurysm
Local dilatation (swelling and weakening) of the wall of a blood vessel, usually the result of atherosclerosis and hypertension; especially serious when occurring in the aorta, when rupture may prove fatal. Abnormal, saclike bulge in the wall of an artery, a vein, or the heart. Sac formed by dilatation of artery, vein, or heart wall.…
-
Aneuploidy
An abnormal number of chromosomes, usually associated with miscarriage, or developmental abnormalities such as Down’s syndrome where there are three copies of chromosome 21 instead of two. Condition in which the number of chromosomes is either more or fewer than normal. The state in which there is an abnormal number of chromosomes: for example, down’s…