Author: Glossary
-
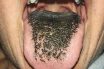
Black tongue disease
A sign of niacin deficiency in dogs, the canine equivalent of pellagra. A disease of dogs. Significant in human health since niacin was discovered in 1937 when it was found to cure black tongue in dogs.
-
Biuret test
A chemical test for proteins based on the formation of a violet colour when copper sulphate in alkaline solution reacts with a peptide bond. A method for measuring protein in the serum. The presence of biuret can be detected by the addition of sodium hydroxide and copper sulfate solutions to the sample. A rose to…
-
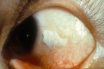
Bitot’s spots
Irregularly shaped foam-like plaques on the conjunctiva of the eye, characteristically in vitamin A deficiency, but not considered to be a diagnostic sign without other evidence of deficiency. Small white spots on the conjunctiva, caused by vitamin A deficiency [Described 1863. After Pierre A. Bitot (1822-88), French physician.] Shiny foam-like spots on the white of…
-
Bisfuran polycyclic compounds
Compounds with several rings including more than two 5-membered oxygen-containing rings.
-
Birth canal
The bony birth canal comprises the passage through the pelvic bones; there is a soft tissue component to the birth canal in the form of the vagina and its supporting tissues. The uterus, vagina and vulva. The widened cervix and vagina through which a baby passes on its way from the uterus during childbirth. Passage…
-
Biological value (BV)
The proportion of absorbed nitrogen that is retained for maintenance and/or growth. An index of protein value or quality that reflects the percentage of absorbed dietary nitrogen used by the body. The efficiency of utilization of a protein by the body, expressed as a percentage of the food nitrogen retained to the food nitrogen absorbed.…
-
Bioinformatics
The application of computational techniques to extract meaning from complex biological data. The utilization of computer science to gather, categorize, and scrutinize biochemical and genetic data.
-
Biofortification
Food fortification achieved by plant breeding or genetic modification to give a higher content of nutrients.
-
Bio-electrical impedance (BIE)
Amethod of measuring the proportion of fat in the body by the difference in the resistance to passage of an electric current between fat and lean tissue.
-
Biocytin
The main form of the vitamin biotin in most foods, bound to the amino acid lysine.