Author: Glossary
-
Halophiles (halophilic bacteria)
Bacteria and other microorganisms able to grow in high concentrations of salt. Descriptive of microorganisms that will grow only if a very high salt concentration is present; salt loving. Those able to withstand the osmotic pressure of very high levels of salt, sugar etc., and as such a hazard of food processing.
-
Halal
Food conforming to the Islamic (Muslim) dietary laws. Meat from permitted animals (in general grazing animals with cloven hooves, and thus excluding pig meat) and birds (excluding birds of prey). The animals are killed under religious supervision by cutting the throat to allow removal of all blood from the carcass, without prior stunning. Food that…
-
Haemosiderin
An iron storage protein.
-
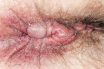
Haemorrhoids (or piles)
Varicosity in the lower rectum or anus due to congestion of the veins; caused or exacerbated by a low-fibre diet and consequent straining to defecate. Painful and swollen anal veins. Haemorrhoids are swollen veins located in the lining of the anus. They can occur near the anal opening, known as external haemorrhoids, or further up…
-
Haemoglobin
The red haem-containing protein in red blood cells which is responsible for the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the bloodstream. A red respiratory pigment formed of haem and globin in red blood cells which gives blood its red colour. It absorbs oxygen in the lungs and carries it in the blood to the…
-
Haematemesis
Vomiting bright red blood, due to bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract. A condition in which someone vomits blood, usually because of internal bleeding. Haematemesis means the vomiting of blood. Blood brought up from the stomach is generally dark in colour and may have been so far digested as to form small brown granules resembling…
-
Haem
The iron-containing pigment which forms the oxygen-binding site of haemoglobin and myoglobin. It is also part of a variety of other proteins, collectively known as haem proteins, including the cytochromes. A molecule containing iron which binds proteins to form haemoproteins such as haemoglobin and myoglobin. An iron-containing porphyrin compound that combines with the protein globulin…
-
Guanine
A purine base. It occurs naturally as a fundamental component of nucleic acids. A purine base found in DNA and RNA. One of the purine bases in DNA and RNA. Purine bases are degraded to urate and excreted in the urine.
-
Growth faltering
A term indicating that a child’s linear or ponderal growth is falling away from the reference trend. This implies that weight or height has been measured at intervals over a period of time.
-

Green revolution
A process in which cereal crop yields increased as a result of farmer adoption of high yielding varieties bred at international agricultural research centres and adapted to local conditions at national agricultural research institutions. Planting of these varieties has coincided with expansion of irrigated area and fertiliser use.