Author: Glossary
-
Nitrogen conversion factor
Factor by which nitrogen content of a foodstuff is multiplied to determine the protein content; it depends on the amino acid composition of the protein. For wheat and most cereals it is 5.8; rice, 5.95; soya, 5.7; most legumes and nuts, 5.3; milk, 6.38; other foods, 6.25. In mixtures of proteins, as in dishes and…
-
Ninhydrin test
For the amino group of amino acids. Pink, purple or blue colour is developed on heating an amino acid or peptide with ninhydrin. A neurological test of sensation following peripheral nerve injury; used to detect a sympathetic response as indicated by sweat.
-
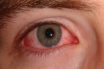
Night blindness
Nyctalopia. Inability to see in dim light as a result of vitamin A deficiency. First symptom of vitamin A deficiency. The individual is unable to adapt to changes in light intensity. It is reversible if the vitamin is provided. Abnormal reduction in vision in darkness, due to deficiency of vitamin A or to retinal disorder;…
-
Nicotinic acid
One of the vitamers of niacin. A B vitamin. Nicotinic acid is a derivative of pyridine and is interchangeable with its amide, nicotinamide. Both forms of the vitamin are equally active. Nicotinamide is a component of the coenzymes NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP, its phosphate. Nicotinic acid is required in the diet but can…
-
Nicotinamide
One of the vitamers of niacin. Nicotinamide, the amide of nicotinic acid, is usually used instead of the latter in the treatment of vitamin B deficiency. A basic amide that is a member of the vitamin B complex, used in the prophylaxis and treatment of pellagra.
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and its phosphate (NAD, NADP)
The coenzymes derived from niacin. Involved as hydrogen acceptors in a wide variety of oxidation and reduction reactions.
-
Niacytin
The bound forms of the vitamin niacin, found in cereals.
-
Niacinogens
Name given to protein-niacin complexes found in cereals.
-
Neuropeptide Y
A peptide neurotransmitter believed to be important in the control of appetite and feeding behaviour, especially in response to leptin. One of the most abundant peptides found in the central and peripheral nervous system. Serves as a vasoconstrictor in conjunction with norepinephrine. It is released by the GI tract and signals hunger. It plays an…
-
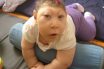
Neural tube defect
Congenital malformations of the brain (anencephaly) or spinal cord (spina bifida) caused by the failure of the closure of the neural tube in early embryonic development. A congenital anomaly which occurs when the edges of the neural tube do not close up properly while the fetus develops in the uterus, e.g. spina bifida. Occurs early…