 Also known as a canker sore, is a type of oral ulcer, which presents as a painful open sore inside the mouth or upper throat.
Also known as a canker sore, is a type of oral ulcer, which presents as a painful open sore inside the mouth or upper throat.
Single or multiple (and often recurrent) transiently painful ulcers in the oral mucous membrane that are usually self-limiting. The cause is unknown and treatment is symptomatic.
Recurrent painful canker sores in the mouth.
Painful ulcers in the mouth area often associated with HIV disease.
A lesion of the skin or mucous membranes (e.g., of the oral mucosa, conjunctiva, or genitalia). It is usually less than 0.5 cm in diameter. If it persists for longer than 2 weeks, it should be biopsied to rule out cancer.
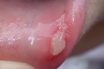
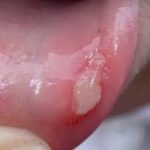
A tiny, discomforting ulcer that emerges individually or in clusters within the inner surfaces of the cheek, lip, or beneath the tongue.
Aphthous ulcers predominantly occur in individuals aged 10 to 40 and tend to impact more women than men. Those who experience the greatest impact often suffer from recurrent ulcers, while others might only have one or two ulcers annually.
The ulcer typically endures for a span of one to two weeks and might result from a heightened sensitivity to haemolytic streptococcus bacteria. Additional factors frequently linked to the emergence of these ulcers include minor injuries, like those from injections or toothbrush abrasions, as well as acute stress and allergies. Among women, aphthous ulcers are more prevalent during the premenstrual phase. Additionally, their likelihood of occurrence might increase if other family members experience recurring ulcerative conditions such as Crohn’s disease.
Typically, each ulcer presents as a small, oval lesion featuring a gray center encircled by a reddened, inflamed halo. These ulcers typically persist for a period of one to two weeks.
Analgesic mouth gels or rinses can provide relief from the discomfort caused by an aphthous ulcer. Certain ointments create a water-resistant barrier that shields the ulcer during the healing phase. These ulcers typically heal on their own, although a physician might recommend a paste containing a corticosteroid medication or a mouthwash with an antibiotic component to expedite the healing process.