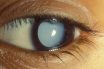
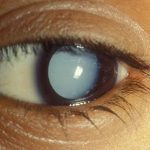
The condition in which the crystalline lens is absent from the eye, usually as a result of surgery.
Absence of the natural lens of the eye, as when a cataract has been surgically removed.
Absence of the natural lens of the eye. In the normal eye, the lens is a clear, crystalline structure located behind the iris (the colored part of the eye) that focuses light coming into the eye. The cause of aphakia can be a congenital abnormality (lacking lenses at birth), an injury that destroys the lens, or surgical removal. Surgical removal of the lens is standard treatment for cataract, a disease in which the lens becomes cloudy or opaque. Aphakia causes extreme farsightedness, which can be treated with glasses or contact lenses or by surgery to insert a plastic lens implant in the eye.
Aphakia refers to the absence of the lens in the eye. This condition can occur congenitally, meaning it is present from birth, or it may arise as a result of surgical interventions like cataract surgery. Additionally, aphakia can occur due to a penetrating injury to the eye.
Aphakia results in significant impairment of focusing ability in the affected eye and necessitates corrective measures. This can be accomplished through the implantation of a lens, the use of contact lenses, or the utilization of eyeglasses. These interventions aim to restore proper vision and compensate for the absence of the natural lens.
The innate lack of the crystalline lens in the eye.